
How IEEE 3005.4-2020 Improves Reliability
Share
IEEE 3005.4-2020 provides detailed guidance to ensure emergency and standby power systems remain reliable during outages. This standard, released in 2020, focuses on improving system performance through proper design, testing, and maintenance practices. It highlights key areas like equipment specification, environmental factors, and ongoing operational checks to prevent failures in critical systems such as those in hospitals or data centers.
Key Takeaways:
- Reliability Metrics: Focuses on failure rates, Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF), and system availability.
- Design Practices: Includes load prioritization, redundancy, and proper equipment selection.
- Testing Procedures: Emphasizes acceptance testing, monthly generator exercises, and transfer switch testing.
- Maintenance Strategies: Recommends regular inspections, fuel quality checks, and battery maintenance.
- Equipment Sourcing: Stresses the importance of rigorous testing for both new and used components.
By following IEEE 3005.4-2020, engineers and facility managers can reduce risks, ensure compliance, and maintain dependable power systems during emergencies.
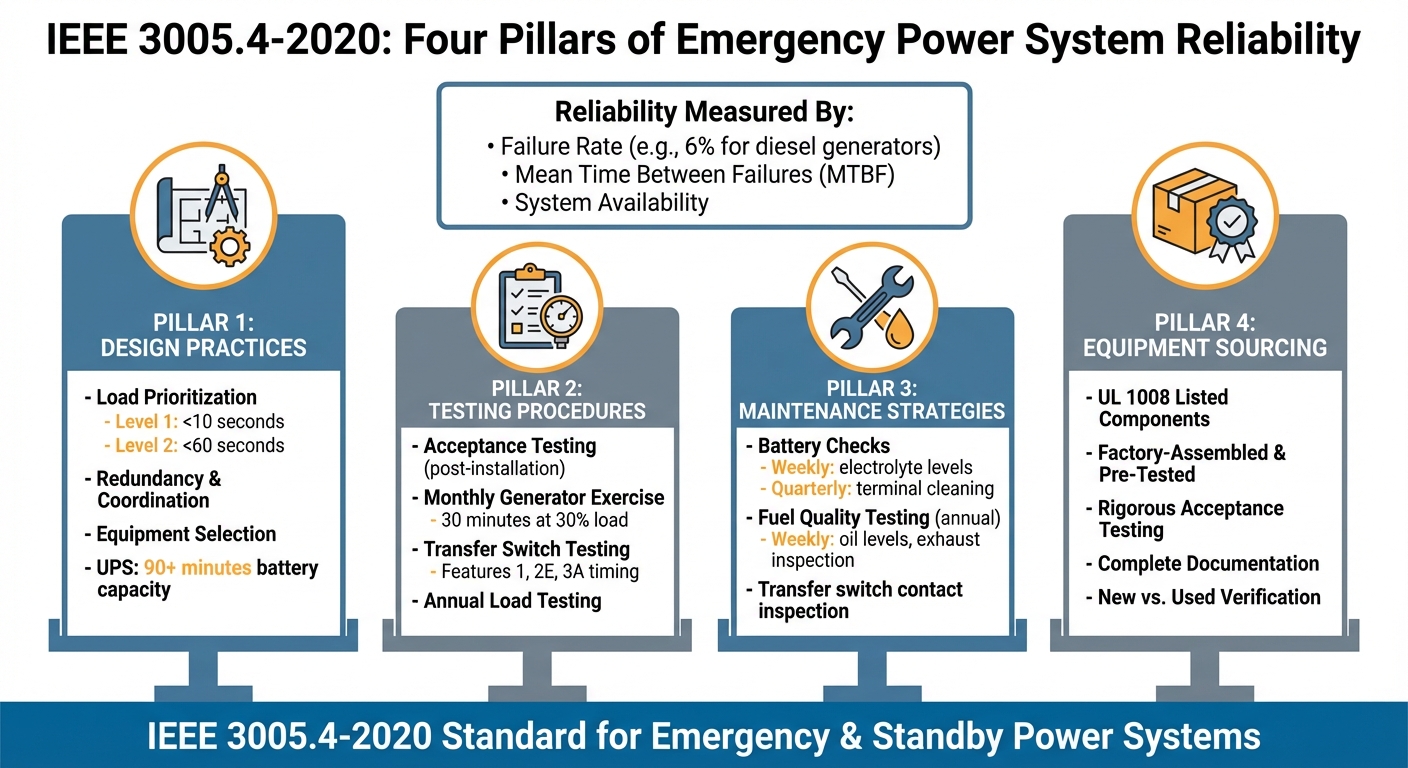
IEEE 3005.4-2020 Four Pillars of Emergency Power System Reliability
Reliability Principles from IEEE 3005.4-2020
Basic Reliability Concepts
According to IEEE 3005.4-2020, reliability refers to a piece of equipment's ability to start and sustain load under specific conditions for a defined period.
Three key metrics are used to measure reliability: failure rate (e.g., diesel generators may have a 6% annual failure rate), Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF), and system availability. These metrics provide a foundation for evaluating how systems perform under expected conditions.
To enhance reliability, redundancy is a common strategy. This involves duplicating critical components so that if one fails, another can seamlessly take over. For instance, interconnected generators can share loads to ensure uninterrupted operation. The standard emphasizes the importance of precise equipment specification and rigorous acceptance testing to prevent reliability issues from the start.
These principles help explain why certain failures are predictable and how they can be mitigated.
Common Causes of Power System Failures
Understanding the root causes of power system failures is essential for improving reliability.
Emergency power systems often fail for reasons that can be anticipated. For example, diesel generators may encounter issues such as failure to start, failure to run and supply load, or becoming unavailable due to maintenance. Environmental factors - like extreme temperatures, high humidity, or exposure to contaminants - can worsen equipment degradation if not accounted for during the design phase.
Incorrect equipment specification is another frequent problem. When equipment is not properly matched to a facility's actual requirements, even well-maintained systems can underperform. Similarly, inadequate acceptance testing during commissioning increases the risk of failures during critical emergencies. To address these challenges, the standard mandates site-specific environmental assessments and thorough testing protocols before systems become operational.
The IEEE 3006 series provides historical reliability data, offering valuable insights into potential weak points that could lead to outages. Additionally, engineers can use probability methods outlined in IEEE 3006.5 to perform detailed reliability analyses, identifying vulnerable components in standby power systems before they cause disruptions.
Design Practices for Better Reliability
Load Acceptance and Coordination
According to IEEE 3005.4-2020, prioritizing load transfer is essential when using paralleled generators. For Level 1 loads, power must be restored within 10 seconds of an outage, while Level 2 loads must be energized within 60 seconds. The standard also requires automatic deactivation of lower-priority loads during component failures to avoid overloading the remaining generators. To implement this effectively, work closely with building owners to categorize loads into Level 1, Level 2, and Optional priorities.
Another key practice is selective coordination of overcurrent protective devices. This ensures that when a fault occurs in one circuit, only the nearest breaker trips, preventing a cascading failure that could lead to a total system blackout. For uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems that serve emergency loads, IEEE 3005.4-2020 typically requires at least 90 minutes of battery capacity to bridge the gap during a power loss.
These practices form the backbone for ensuring reliable power delivery and help guide the selection of equipment that meets demanding reliability standards.
Selecting Proven Standard Products
Once load coordination is in place, the next step is choosing reliable, time-tested equipment. IEEE 3005.4-2020 emphasizes the importance of using factory-assembled, pre-tested, and listed equipment. For example, automatic transfer switches should be UL 1008 listed, ensuring they can reliably manage load transfer operations.
The standard provides a clear roadmap for improving emergency and standby power system reliability through precise specifications, rigorous testing, and ongoing maintenance. The IEEE 3000 Standards Collection is a valuable resource for selecting components that meet strict technical requirements. Specific standards, like IEEE 3004.3 and IEEE 3004.5, offer detailed guidance to optimize system reliability. Additionally, historical data from the IEEE 3006 series can help identify products with proven performance in similar scenarios.
It’s important not to rely solely on manufacturer claims. Instead, conduct thorough acceptance testing as outlined in the standard to verify that the equipment performs as expected. This approach ensures that every component contributes to the system's overall reliability.
Testing Procedures in IEEE 3005.4-2020
Testing plays a crucial role in maintaining system reliability, acting as the bridge between design practices and ongoing maintenance routines.
Testing Automatic Transfer Equipment
According to IEEE 3005.4-2020, acceptance testing must be conducted immediately after installation to confirm the performance of the Emergency Power Supply System (EPSS). For automatic transfer switches, this involves ensuring that all critical timing features function as intended.
Start by setting the bypass to "Normal" and the isolation switch to "Connected". Use appropriate meters to verify that both emergency and normal source voltages, as well as phase rotations, align correctly. This step is vital for safeguarding three-phase motors. Monthly testing should simulate a normal power outage using the transfer switch controls, ideally aligning with generator exercise sessions.
Focus on key timing features during these tests:
- Feature 1: Handles momentary outages (0–6 seconds).
- Feature 2E: Manages delays in emergency transfer.
- Feature 3A: Ensures retransfer after the system stabilizes.
After retransfer, confirm the generator completes its unloaded engine cool-down period before shutting down. Annual maintenance should include inspecting and cleaning the main contacts, along with testing voltage-sensing relays to ensure they correctly detect power loss at the preset dropout and pickup levels.
These detailed procedures provide a thorough assessment of diesel generator performance and system readiness.
Emergency Power Supply Testing
Diesel generators must be exercised monthly for at least 30 minutes at a load of 30% of their nameplate kW rating. This ensures they are ready to start and operate reliably. Running the generator at this load is critical to avoiding "wet stacking", a condition where unburned fuel and carbon accumulate, potentially damaging the engine.
"The 30-minute monthly test requirement must be conducted under a 30% kW load based on the standby kW rating on the nameplate, or by monitoring the exhaust gas temperatures as recommended by the manufacturer." – EC&M
If the actual load falls below 30%, supplemental load banks should be used to achieve the proper engine temperature. Weekly checks of starting batteries should include monitoring electrolyte levels (Level 1), while quarterly checks should ensure terminal tightness. Additionally, because diesel fuel deteriorates over time, annual testing for water and contaminants is necessary to avoid fuel injector issues. If any repairs or replacements are made, an operational test must follow. This test should run the system on alternate power for at least 30 minutes to confirm proper functionality.
sbb-itb-501186b
Maintenance Strategies from the Standard
Routine Maintenance for Critical Systems
The IEEE 3005.4-2020 standard emphasizes the importance of starting a scheduled maintenance program as soon as equipment passes acceptance testing. Such a program is key to uncovering and addressing hidden issues in standby systems before they lead to failures.
"The continued reliability of the EPSS is dependent on an established program of routine maintenance and operational testing." – Curtis Power Solutions
Battery issues are the leading cause of generator failures. For Level 1 systems, weekly checks of electrolyte levels are recommended, along with quarterly cleaning and tightening of terminals. Monthly health tests, using either specific gravity or conductance measures, are also essential.
Fuel system maintenance is another critical area. Annual tests following ASTM D 975 guidelines help detect water, contaminants, or microbial growth in the fuel supply. Weekly checks of lube oil levels and ensuring the oil heater is functioning - especially in colder conditions - are also advised. Additionally, visually inspect the exhaust system and condensate drains weekly to prevent performance issues.
Transfer switch upkeep involves annual inspections of main contacts to check for signs of overheating or erosion, as well as ensuring all wiring is secure. Automatic transfer switches should be tested monthly, and it’s a good practice to store duplicate instruction manuals securely off-site for quick reference if needed.
Using IEEE 3007 Maintenance Recommendations
To build on routine maintenance, IEEE 3007 provides detailed guidelines that complement IEEE 3005.4-2020. While 3005.4 highlights what needs to be maintained for overall system reliability, IEEE 3007 dives into specific procedures for maintaining individual electrical components.
Combining these standards ensures maintenance programs target known failure risks, such as battery degradation or fuel contamination. For Level 1 systems, annual circuit breaker exercises and a full-duration load test every 36 months are recommended to confirm these systems meet their Class rating. Additionally, storing critical spare parts and specialized tools in a dedicated cabinet within the generator room ensures quick access during emergencies. All maintenance and testing should be carried out by qualified personnel to ensure compliance with the standards.
Equipment Sourcing with IEEE 3005.4-2020
Building on earlier discussions about design, testing, and maintenance, sourcing the right equipment is another critical step in ensuring compliance with IEEE 3005.4-2020 while boosting system reliability.
New vs. Used Equipment for Reliability
Deciding between new and used components can significantly influence system reliability. IEEE 3005.4-2020 emphasizes the importance of rigorous acceptance testing for both options.
| Feature | New Equipment | Used/Refurbished Equipment |
|---|---|---|
| Reliability Verification | Manufacturer-certified to meet current IEEE 3005.4-2020 standards | Must undergo acceptance testing to verify reliability |
| Maintenance Documentation | Baseline established at installation | Relies on existing operations and maintenance records |
| Environmental Compliance | Can be customized to meet specific environmental needs | Requires verification for compatibility with site conditions |
| Availability | May involve longer lead times for specialized components | Often available immediately via platforms like Electrical Trader |
| Cost Consideration | Higher upfront investment | Lower cost, allowing budget flexibility for redundancy or improved maintenance |
This comparison highlights key factors that influence both reliability and procurement strategies.
According to IEEE 3005.4-2020, reliability improvements depend on factors such as the equipment's intended application, environmental conditions, detailed specification and acceptance testing, and strong maintenance practices. For used components, particularly those sourced through platforms like Electrical Trader, comprehensive maintenance records are essential. Battery-related failures, for instance, are a frequent issue that underscores the need for proper documentation.
These considerations are pivotal when making procurement decisions that align with IEEE 3005.4-2020 standards.
Procurement Practices for Standard Compliance
To meet IEEE 3005.4-2020 requirements, thorough verification and documentation are key.
Before purchasing any equipment - whether new or used - prepare a detailed specification document outlining operating conditions and load requirements. This ensures the selected equipment, such as generators, transformers, or transfer switches, aligns with your system's reliability goals.
For used equipment, insist on complete documentation, including maintenance logs, testing records, and environmental ratings. Ensure sellers provide all necessary technical details to allow a comprehensive evaluation before purchase.
Consider sourcing redundant components if a single point of failure is identified. The cost savings from purchasing used equipment through Electrical Trader can offset the expense of redundancy. However, strict acceptance testing should be applied to any refurbished items, such as transfer switches, breakers, or transformers, before they are integrated into your emergency power supply system.
Conclusion
Key Takeaways
The IEEE 3005.4-2020 standard offers a structured approach to enhance the reliability of emergency and standby power systems. It focuses on four essential areas: specific application requirements, environmental considerations, thorough specification and acceptance testing, and ongoing operations and maintenance.
Maintaining reliability requires continuous attention. Systems classified as Level 1 or Level 2 come with strict timing requirements for power restoration. This means prioritizing critical loads, ensuring physical separation between emergency and normal circuits, and reducing single points of failure.
Acceptance testing plays a key role in confirming that equipment functions as expected before being put into operation. Meanwhile, well-defined maintenance strategies ensure systems are always ready for unexpected outages. Whether you’re working with new components or refurbished equipment, IEEE 3005.4-2020 provides the tools to assess reliability and meet compliance standards. These principles encourage taking proactive steps to strengthen system performance.
Next Steps
Start by classifying your system early in the design process. Identify whether it falls under Level 1 (life safety) or Level 2 (standby) to apply the appropriate reliability and testing standards. Align your design with NFPA guidelines to meet both technical and regulatory requirements. When purchasing equipment - whether it’s brand new or refurbished - use the standard’s testing protocols to ensure compliance. Rely on established maintenance and testing practices to validate system performance. Resources like Electrical Trader can help you source compliant components, including generators, transfer switches, transformers, and breakers.
FAQs
How does the IEEE 3005.4-2020 standard enhance the reliability of emergency and standby power systems?
The IEEE 3005.4-2020 standard focuses on improving the reliability of emergency and standby power systems by providing detailed guidance on system design, operation, and maintenance. It highlights essential practices like choosing the right equipment, conducting regular testing, and accounting for factors that could affect system performance.
Adhering to these guidelines helps organizations reduce downtime, strengthen system reliability, and ensure consistent power delivery during critical moments. This makes IEEE 3005.4-2020 a key reference for maintaining dependable emergency power systems.
What testing procedures does IEEE 3005.4-2020 recommend for improving power system reliability?
IEEE 3005.4-2020 provides a detailed framework for testing emergency and standby power systems to ensure they perform reliably when needed most. The standard highlights three main types of testing:
- Environmental Testing: Evaluates how the system operates under different conditions, such as temperature changes or humidity levels, ensuring it can handle real-world scenarios.
- Specification and Acceptance Testing: Verifies that the equipment meets the required standards and specifications before being put into operation.
- Operational Testing: Simulates critical scenarios to confirm that the system functions as intended during emergencies.
By implementing these testing procedures, organizations can catch potential problems early, improve overall reliability, and maintain compliance with established industry standards.
Why is specifying equipment important for reliable emergency and standby power systems under IEEE 3005.4-2020?
Specifying the right equipment is crucial for ensuring the reliability of emergency and standby power systems, as detailed in IEEE 3005.4-2020. A well-thought-out specification guarantees that every component is tailored for its intended use, capable of handling the environmental conditions it will encounter, and able to meet strict acceptance testing requirements.
Following these standards helps enhance the dependability, safety, and overall performance of power systems, reducing the chances of failure when they are needed most.
