
How Remote Monitoring Improves Emergency Power Systems
Share
Emergency power systems like generators, UPS, and transfer switches are critical during outages. Remote monitoring enhances their reliability by providing real-time data on system health, such as fuel levels, battery status, and engine performance. It uses secure connections (cellular, satellite, or Ethernet) to send alerts via SMS, email, or calls, enabling faster issue detection and resolution. This reduces downtime, prevents costly repairs, and helps facilities meet safety and regulatory standards.
Key benefits include:
- Continuous Monitoring: Tracks fuel, battery health, temperature, and more.
- Predictive Maintenance: Identifies issues early, avoiding failures.
- Cost Savings: Cuts unnecessary service calls and downtime.
- Regulatory Compliance: Automates reporting to meet U.S. standards.
- Remote Control: Allows starting equipment or running diagnostics off-site.
Facilities like hospitals and data centers rely on these systems to avoid risks during outages. Proper setup involves evaluating equipment, selecting compatible hardware, and configuring secure alerts and dashboards.
Core Features of Remote Monitoring Systems
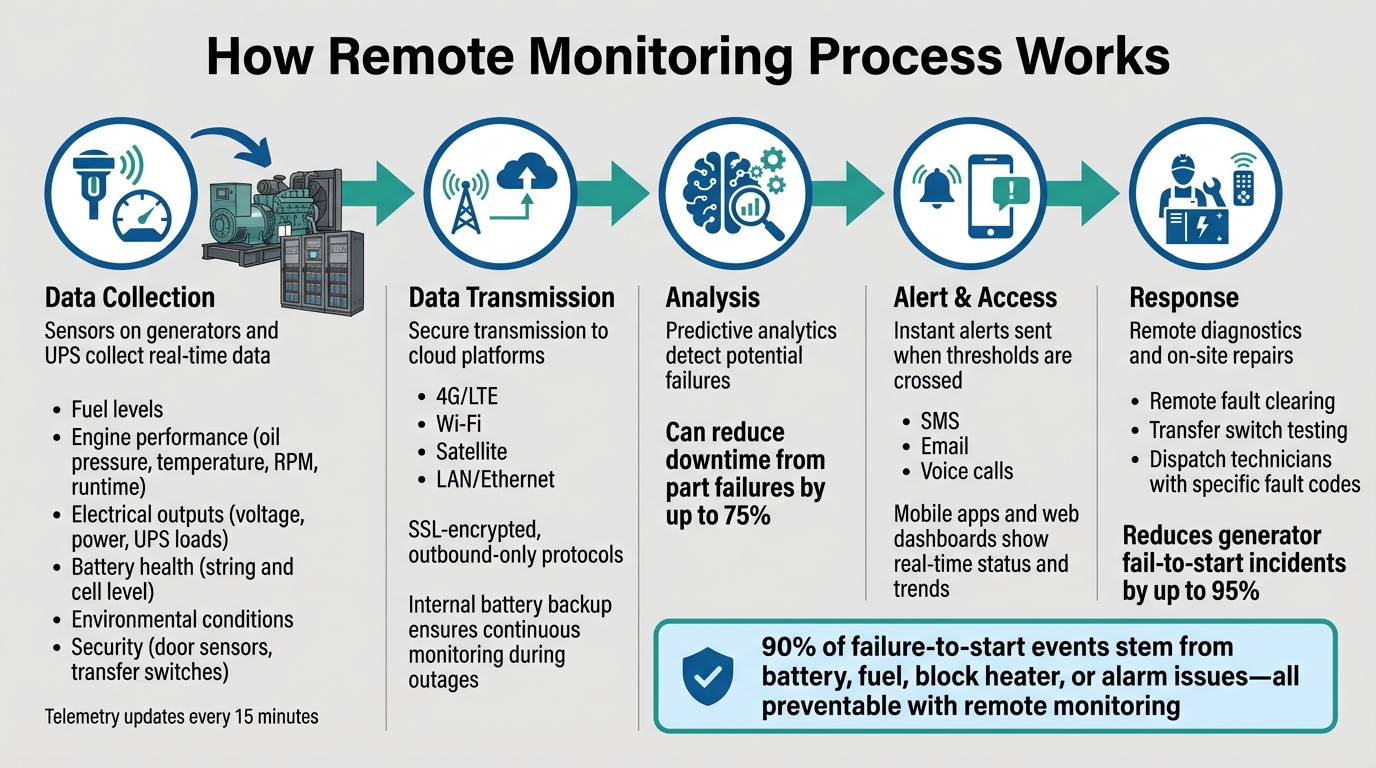
How Remote Monitoring Systems Work for Emergency Power Equipment
Data Points Monitored by Remote Systems
Remote monitoring systems track a wide range of critical metrics, including fuel levels, engine performance, electrical outputs, battery health, environmental conditions, and site security. These systems measure engine parameters like oil pressure, temperature, runtime hours, and RPM, while also monitoring electrical outputs such as voltage, power, and UPS loads. Battery performance is assessed at both the string and individual cell levels. Additionally, they keep an eye on ambient conditions and key components like capacitors, fans, and air filters. For security, door sensors and transfer switch indicators are monitored.
Advanced systems go a step further, incorporating theft alarms for fuel, precise voltage diagnostics for individual battery cells, and environmental sensors to prevent overheating. The level of detail in these measurements is crucial. In fact, integrating remote monitoring with predictive analytics can slash downtime from part failures by as much as 75%. Some systems even update telemetry every 15 minutes, offering near real-time insights.
All these metrics play a vital role in the monitoring process described below.
How the Monitoring Process Works
Generators and UPS systems are equipped with sensors that collect real-time data. This information is transmitted through 4G/LTE, Wi-Fi, satellite, or LAN connections to cloud-based platforms. Predictive analytics then analyze the data to detect potential failures. Users can access site trends and statuses on mobile apps or web dashboards, while alerts are sent via SMS, email, or voice calls when any parameter crosses a set threshold. Technicians can remotely clear faults or test transfer switches when necessary.
To ensure uninterrupted monitoring, these systems often include internal battery backups. This feature enables them to continue operating and sending alerts even during primary power outages. For example, in 2023, Kaiser Permanente's Senior Manager, Bitsy Bernat, shared how their monitoring system helped prevent a major issue by identifying a temperature spike in a facility:
"The service has definitely quickly deployed field technicians. At one of our sites, the temperature in the room was rising. Because we received a notification, we were able to get an engineer dispatched to the site to the HVAC problem. Had we not done that, we might have ended up with a UPS failure."
- Bitsy Bernat, Senior Manager, Kaiser Permanente
This seamless data transmission and alert system naturally demand robust security and reliability measures, which are covered next.
Data Security and System Reliability
The effectiveness of any monitoring system hinges on the strength of its data security measures.
To mitigate risks, data is transmitted outbound using SSL-encrypted protocols like SMTP, eliminating the need for inbound firewall access. Cellular or satellite connectivity ensures isolation, while multi-level authentication and detailed access logs limit system access. Redundant communication paths and backup hardware further enhance reliability, reducing generator fail-to-start incidents by up to 95%.
Some providers take extra precautions by designing systems that are read-only, removing the ability for remote control of critical power infrastructure. When evaluating providers, it’s wise to prioritize systems that use outbound-only data transfers and offer two-step verification for web-based access. These measures ensure both security and operational reliability.
Benefits of Remote Monitoring for Emergency Power
Preventive Maintenance and Less Downtime
Remote monitoring keeps a close eye on the health of essential components like batteries, fans, and capacitors. Instead of sticking to a rigid replacement schedule, it allows for swapping parts based on their actual condition, reducing unnecessary maintenance.
Here's a striking statistic: about 90% of failure-to-start events in emergency power systems stem from issues with batteries, fuel, block heaters, or alarms. For example, if a battery charger fails, the voltage can dip below the 11.0 V cranking threshold in just one day. With remote monitoring, this issue can be flagged a full day in advance, giving you time to act.
Jarrett, Founder and Vice President of OmniMetrix LLC, highlights the importance of addressing these common issues:
"90% of failure-to-start events can be attributed to these four situations [battery, fuel, block heaters, and ignored alarms]. Then, prompt attention can prevent 90% of would-be emergency power system failures."
By catching these problems early, remote monitoring ensures faster fault detection and smoother resolutions.
Quicker Problem Detection and Response
Imagine getting instant alerts - via SMS, email, or phone - about faults in your emergency power system, even at unmanned sites. These alerts provide specific fault codes, enabling technicians to show up prepared and ready to fix the issue.
Remote monitoring goes a step further by distinguishing between minor glitches and serious faults. This means operators can remotely diagnose and even reset issues when necessary. According to Jarrett:
"In the 50% of alarms that are simply transients, the owner's standby power can be recovered quickly via this remote service attention."
Additionally, these systems monitor utility power quality, helping detect if a generator is running unnecessarily due to erratic voltage instead of an actual outage. This prevents excessive fuel use and reduces wear and tear on the engine.
Lower Costs and Better Operations
Remote monitoring doesn't just make problem-solving faster - it also saves money and improves overall system performance.
By catching potential failures early, predictive analytics can cut equipment downtime from part failures by up to 75%. Fewer unnecessary service calls mean lower costs, and technicians can arrive with the right parts, boosting first-time fix rates and reducing labor hours. Addressing small issues quickly also avoids expensive repairs down the line.
Automated reporting tools track fuel usage, runtime, and emissions, ensuring compliance with EPA and state regulations. This helps facilities avoid hefty fines while streamlining operations for multi-generator setups through centralized dashboards. Some providers, like Eaton, even offer free 90-day trials for services like PredictPulse, giving facilities a chance to test the technology before committing.
Step-by-Step Guide to Installing Remote Monitoring
If you're looking to harness the benefits of real-time data and fault detection for your emergency power systems, this step-by-step guide will help you set up a remote monitoring system tailored to your needs.
Evaluating Your Current Equipment and Requirements
Start by taking stock of all your equipment - backup generators, UPS batteries, fuel tanks, and HVAC units. Check if your devices support MODBUS or SNMP outputs, as these protocols are key for detailed diagnostics. For example, MODBUS can provide accurate fuel level readings without needing extra sensors.
Next, determine the number of inputs you'll need. Discrete inputs handle binary alarms (like on/off statuses), while analog inputs are used for continuous data like voltage, temperature, or fuel levels. Using a standardized survey worksheet can help you organize this information.
Andrew Erickson, an Application Engineer at DPS Telecom, offers this advice:
"First, decide what you want to monitor - generator, temperature, door sensors - and then we'll add those up. The total determines which RTU you need."
Don't forget to assess your site's physical setup. Note the available power sources (e.g., –48V DC or +24V DC), mounting options (rack, DIN rail, or wall), and connectivity (LAN or cellular). It's wise to plan for a 15–20% capacity margin to accommodate future needs.
Once you've mapped out your equipment and input requirements, you're ready to move on to selecting the right hardware and network solutions.
Selecting Hardware and Network Connections
For smaller sites, look for RTUs with around 16 discrete inputs and 6 analog inputs. Larger setups may require RTUs with 64 discrete and 8 analog inputs. Make sure the hardware supports analog sensors (0–5 VDC or 4–20 mA) and digital protocols like MODBUS via RS-485.
Whenever possible, prioritize wired Ethernet connections. According to Andrew Erickson:
"Opt for wired connections over wireless when possible, as they typically offer greater reliability and performance. Network security is another factor that drives virtually all of my clients to wired connections."
For remote locations without wired infrastructure, cellular connectivity is a solid alternative. Many RTUs are equipped to automatically switch to cellular modems if the primary LAN connection fails, ensuring secure data transmission. If you're ordering generators, make sure the manufacturer includes the necessary hardware or software for MODBUS, as some opt for proprietary cloud services instead.
Once your hardware and network are in place, it's time to configure alerts and dashboards to complete your system.
Setting Up Alerts, Dashboards, and Response Procedures
Define high and low thresholds for each sensor, and set up multi-channel notifications through email, SMS, or phone. Include an acknowledgment system to ensure alerts escalate if they're not addressed.
For operations managing more than 10 remote sites, consider using a master station. This consolidates alarms into one interface, eliminating the need to monitor individual RTU webpages. Your dashboard should display real-time statuses, geographic maps for tracking sites, and historical trend graphs to analyze patterns. Implement multi-level security so team members only see the alerts and data relevant to their roles or regions.
Finally, review alarm data regularly to identify and resolve recurring nuisance alarms. This step helps reduce alarm fatigue and ensures your team stays focused on critical issues.
sbb-itb-501186b
Compliance, Security, and Equipment Sourcing
Meeting U.S. Electrical and Safety Standards
When it comes to emergency power systems, compliance with U.S. electrical and safety standards is non-negotiable. For instance, NFPA 110 requires dual annunciation for Level 1 systems - those where failure could lead to loss of life or serious injury. Similarly, the NEC mandates dual shutdowns for generators exceeding 15 kW and specifies ground-fault alarms instead of automatic disconnection.
NFPA 99 emphasizes that remote monitoring should enhance, not replace, hard-wired annunciators. Additionally, IBC Section 911 calls for generator annunciation to be installed in fire command centers. If you’re setting up monitoring equipment, ASCE 24 provides guidance on placement above base flood elevations, particularly for hospitals and other Group I-2 facilities.
These standards collectively ensure that remote monitoring systems contribute to reliable and compliant emergency power solutions.
Protecting Data and Ensuring Reliable Communication
Data security and communication reliability are critical for remote monitoring systems. One key measure is network separation - keeping IT and OT networks isolated minimizes the risk of breaches spreading across systems. To safeguard data, employ firewalls, VPNs, and encryption. For added resilience, ensure wired Ethernet connections can automatically switch to cellular modems when needed.
When selecting monitoring systems, prioritize those that support encrypted data transfer, especially if your facility uses cloud platforms or wireless networks. Additionally, verify that the system integrates seamlessly with your existing infrastructure, such as SNMP managers, or offers standalone alerts via email and SMS.
Strong security measures and clear communication protocols are essential for sourcing components that align with compliance and operational needs.
Finding Components Through Electrical Trader
Sourcing the right components is just as important as meeting compliance and security standards. Start by confirming whether your generator supports MODBUS or discrete contact closures - MODBUS is often preferred for precise fuel-level diagnostics. Additionally, check your site’s power and mounting requirements before making a purchase.
Platforms like Electrical Trader (https://electricaltrader.com) simplify the process by offering a centralized marketplace for both new and used electrical components. Their catalog includes essentials like breakers, transformers, transfer switches, and power generation equipment, all designed to meet NFPA 110, NEC, and IBC standards. Whether you’re looking for an emergency standby diesel generator or components tailored to specific voltage needs, their categorized listings make it easy to find what you’re looking for.
For more specialized hardware like RTUs and annunciators, consider working with manufacturers that provide custom solutions. As Andrew Erickson, an Application Engineer at DPS Telecom, explains:
"Off-the-shelf solutions... are often the smart play when your site parameters match up well. But remember that... we keep a custom-engineering team in-house for the other 20% of projects that need special capacity, new form factors, or unique I/O signals."
Conclusion
Remote monitoring has redefined how emergency power systems operate by enabling real-time data tracking, predictive maintenance, and quicker response times. Instead of waiting for equipment failures, these systems continuously monitor critical metrics such as fuel levels, battery performance, and engine temperature, refreshing every 15 minutes. This constant insight allows technicians to diagnose issues remotely and arrive on-site with the right tools and parts, cutting down on both downtime and repair costs.
By addressing minor problems before they escalate, remote monitoring minimizes the risk of costly repairs and lengthy outages. For facilities where downtime can lead to lost revenue, equipment damage, or even regulatory penalties, this proactive approach offers an extra layer of protection.
The role of high-quality components cannot be overstated. Reliable system performance starts with sourcing dependable parts. For example, robust sensors prevent chain reactions, like a single faulty battery cell compromising an entire backup system. Secure connectivity, such as LTE wireless with outbound-only data transfer, ensures alerts are delivered to the right personnel - even if local networks are down - while also guarding against cyber threats. Automated reporting further simplifies compliance with state and federal regulations by generating audit-ready logs without extra manual effort.
When assembling or upgrading your monitoring system, it's crucial to verify that the hardware supports MODBUS for detailed diagnostics and complies with standards like NFPA 110, NEC, and IBC. Platforms such as Electrical Trader (https://electricaltrader.com) provide a convenient marketplace for sourcing breakers, transformers, transfer switches, and other power generation equipment. Whether you're enhancing an existing setup or starting from scratch, investing in compliant, high-quality components ensures that your emergency power systems remain dependable when you need them most.
FAQs
How does remote monitoring improve the reliability of emergency power systems?
Remote monitoring boosts the dependability of emergency power systems by offering real-time insights into key components such as oil pressure, engine temperature, battery voltage, fuel levels, and run-time. Using sensors, these systems constantly gather data and send immediate alerts when any parameter slips outside its safe range. This proactive approach helps address potential issues before they escalate into system failures.
Alerts are sent via SMS, email, or push notifications, allowing technicians to remotely diagnose problems, confirm repairs, and even perform remote start or shutdown operations. This not only cuts down on downtime but also reduces expensive on-site visits. Regular maintenance tasks like fuel treatment or weekly generator tests are also managed more effectively, preventing up to 90% of start-up failures caused by neglected upkeep.
For facilities across the U.S. aiming to upgrade, Electrical Trader provides a variety of remote-monitoring solutions. These options can integrate seamlessly with existing generators or UPS units, making it easier to optimize the performance of emergency power systems.
How is data kept secure in remote monitoring systems for emergency power equipment?
Remote monitoring systems employ a layered security strategy to keep data safe and accessible only to authorized users. These platforms often use cloud-based analytics, combining strict access controls with end-to-end encryption (via TLS/SSL protocols) to protect data during transmission. This ensures that critical information from equipment like generators or UPS systems remains secure and cannot be intercepted or tampered with.
To further reinforce security, these systems typically implement multi-factor authentication for user logins and rely on outbound-only communication, minimizing potential vulnerabilities. Dedicated security teams continuously monitor for threats, enabling real-time detection and response. Additional safeguards, such as role-based permissions, audit logs, and secure firmware updates, help prevent unauthorized changes. Together, these measures provide trustworthy, tamper-resistant oversight of your emergency power systems while adhering to U.S. data protection standards.
How does predictive maintenance help reduce downtime and costs?
Predictive maintenance takes the guesswork out of equipment care by moving from a reactive mindset to a proactive strategy. With the help of remote monitoring sensors - tracking factors like vibration, temperature, or battery health - real-time data flows into advanced analytics systems. These systems can pinpoint potential problems early, giving technicians the opportunity to address issues during scheduled maintenance rather than scrambling to fix unexpected failures. This approach keeps emergency power systems running smoothly and ensures critical loads stay protected.
By basing maintenance schedules on actual equipment performance, facilities can cut down on labor costs and eliminate the need for costly emergency repairs or overtime. Addressing wear and tear early not only extends the life of equipment but also reduces the frequency of urgent part replacements, ultimately lowering overall ownership expenses. In fact, remote monitoring has been shown to prevent up to 90% of failure-to-start events - often caused by battery, fuel, or block-heater issues - saving both time and money.
For predictive maintenance to work effectively, facilities need reliable sensors, UPS units, and spare parts. Electrical Trader offers an extensive selection of new and used electrical components, making it simple to equip emergency power systems with the tools necessary for dependable monitoring and upkeep.
