
IEC 62040-1 for Backup Power Systems
Share
Looking for safety standards for backup power systems? Here's what you need to know:
- IEC 62040-1 is a global standard for Uninterruptible Power Systems (UPS), focusing on electrical, thermal, and mechanical safety.
- In the U.S. and Canada, UL 1778 is the required standard, emphasizing fire safety and compliance with local building codes.
- Manufacturers often seek dual certification (IEC 62040-1 and UL 1778) to meet both international and North American requirements.
Key Takeaways:
- IEC 62040-1 is recognized internationally but doesn't fully satisfy U.S. regulations.
- UL 1778 certification is mandatory in North America to avoid installation delays or penalties.
- Dual-certified equipment simplifies compliance for projects spanning multiple regions.
Understanding these standards ensures your UPS systems meet safety and regulatory needs wherever they're installed.
1. IEC 62040-1
Electrical Safety
IEC 62040-1 establishes stringent guidelines to minimize the risk of electric shock and energy hazards associated with UPS equipment. These regulations apply to most commercial and industrial installations, ensuring safety for anyone who interacts with such systems.
In 2017, IEC 62040-1 replaced the earlier IEC 60950-1 standard with IEC 62477-1 to better address the demands of modern, high-power UPS systems. This update aligns safety protocols with the operational realities of today's equipment. The standard provides detailed instructions on wiring, connections, and ground-fault protection to reduce the risk of electrical accidents during both regular use and maintenance. These measures also help lay the groundwork for managing heat-related risks.
Thermal Safety
Managing heat is a key focus of IEC 62040-1, as it addresses the dangers of fire and overheating in backup power systems. The updated standard includes revised temperature rise tables that define the maximum permissible heat levels for internal components during operation. These guidelines ensure that UPS units can handle their load without overheating, which could otherwise lead to performance issues or even catastrophic failures.
Battery compartments receive special attention due to the risks associated with hydrogen gas. To prevent explosions, the standard specifies requirements for ventilation design and sets strict limits on hydrogen concentration levels. Manufacturers are also required to integrate temperature monitors to detect and address overheating risks. Beyond thermal management, the standard includes measures to protect against hazardous backfeed scenarios.
Backfeed Protection
Backfeed protection is one of the critical safety measures outlined in IEC 62040-1. This feature ensures that when the main AC power is disconnected, no hazardous voltage from the UPS batteries flows back to the input terminals. Without this safeguard, technicians working on upstream electrical systems could face serious risks of electrocution if the UPS remains energized during a power outage.
To ensure compliance, the standard includes a specific backfeed protection test. This test verifies that UPS systems can promptly isolate their internal power sources from the input terminals. Backfeed protection is particularly vital in environments where multiple technicians may be working on different sections of the electrical distribution system at the same time.
Mechanical and Environmental Safety
Beyond electrical and thermal protections, IEC 62040-1 also addresses mechanical and environmental risks to ensure the safe and reliable operation of UPS systems. The standard outlines requirements to mitigate mechanical hazards that could occur during installation, use, or maintenance. These include specifications for enclosure stability, resistance to physical damage, and safeguards against moving parts. The requirements vary depending on whether the equipment is installed in areas accessible to operators or restricted-access locations.
The standard also emphasizes the importance of adhering to the manufacturer's installation and maintenance instructions to maintain compliance. This is especially crucial when purchasing equipment from sources like Electrical Trader, where verifying that used UPS units meet current safety standards can help prevent potential liability issues.
sbb-itb-501186b
2. UL 1778
Electrical Safety
In North America, UL 1778 serves as the key safety standard for UPS systems, complementing the IEC 62040-1 standard discussed earlier. This standard is harmonized with CSA C22.2 No. 107.3, but it takes a slightly different approach. While IEC 62040-1 relies on IEC 62477-1 for safety guidelines, UL 1778 (5th Edition) is based on IEC 60950-1, which focuses on IT equipment safety. This creates a structural difference between the two standards, as IEC 62477-1 is centered on power electronic converters.
UL 1778 requires manufacturers to perform routine production tests on every UPS unit. These tests include dielectric voltage-withstand tests and grounding continuity tests, particularly for cord-connected devices (Annex PPP). Additionally, it mandates proper separation of conductors from different circuits, both within the UPS system and at terminal points (Clause 3.1.4.101).
Thermal Safety
To address potential thermal hazards, UL 1778 emphasizes safety measures like caution labels for non-isolated battery supplies and detailed handling instructions for vented batteries. The standard also outlines requirements for effective cooling systems, proper ventilation, and temperature monitoring to prevent overheating. These measures align with North American fire safety codes. While both UL 1778 and IEC 62040-1 aim to prevent thermal risks, UL 1778 places greater focus on fire safety and electrical insulation.
Backfeed Protection
UL 1778 allows the use of external isolators for backfeed protection, provided that the installation instructions clearly specify the need for external isolation (Clause 2.1.101). When backfeed protection depends on external components - such as a remote shunt-trip or mechanical disconnect - manufacturers are required to include detailed interconnection instructions in the installation manual (Annex FFF). This approach contrasts with IEC 62040-1, which typically incorporates backfeed protection directly into the system as an integrated safety feature.
Mechanical and Environmental Safety
For mechanical safety, UL 1778 outlines construction standards to prevent accidental contact with hazardous parts, particularly through enclosure openings (Clause 4.6). It also specifies requirements for short-circuit fault current markings (Clause 5.101) and testing protocols for units designed to handle high fault current ratings (Annex MMM/NNN). In terms of battery protection, the standard requires Branch Circuit Protection (BCP) for permanently connected battery cabinets.
When purchasing used equipment, such as from Electrical Trader, verifying compliance with UL 1778 ensures your UPS system meets North American safety standards. These requirements are specifically tailored to local installations, focusing heavily on fire safety and electrical insulation. This makes UL 1778 distinct from IEC 62040-1, which integrates safety features more directly into the system design.
Pros and Cons
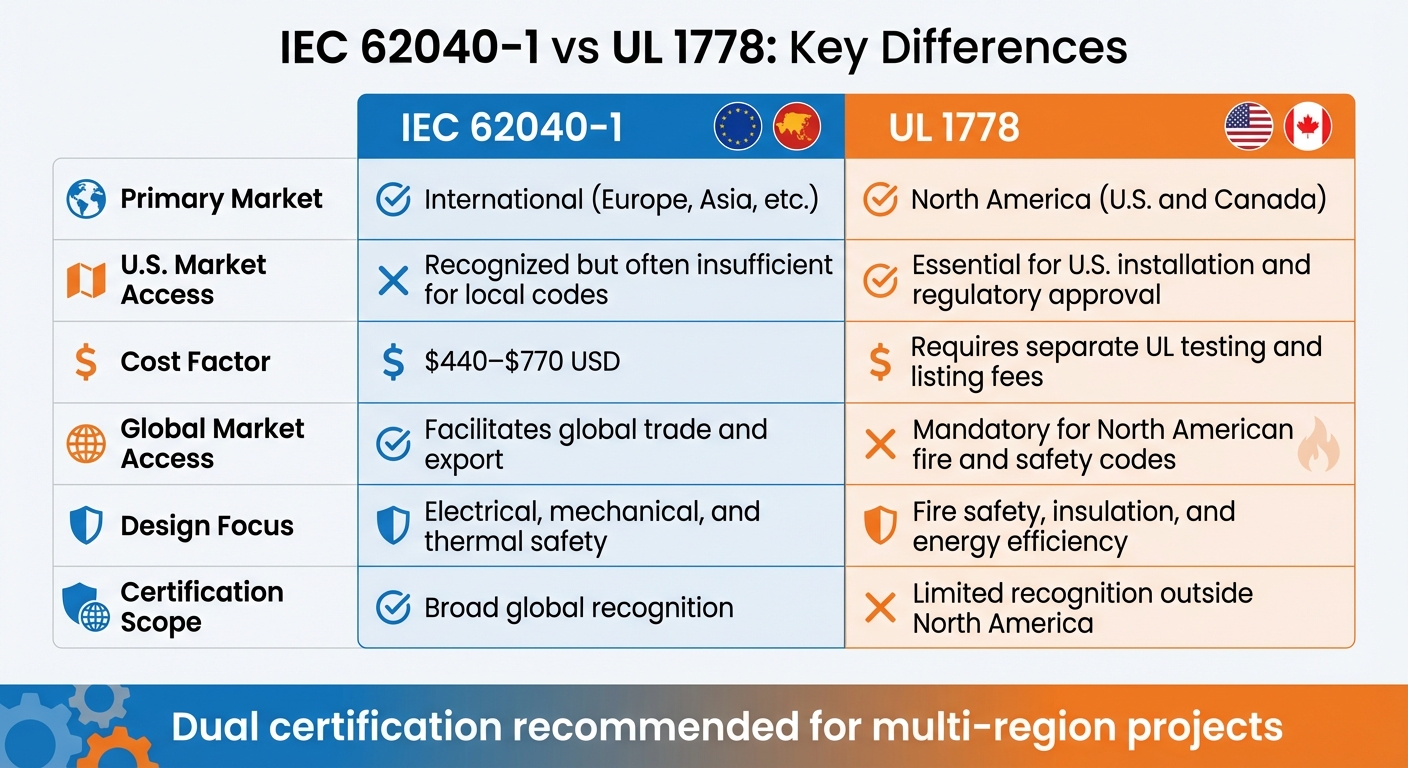
IEC 62040-1 vs UL 1778 UPS Safety Standards Comparison
Choosing the right certification depends heavily on where the installation will take place. Here's a side-by-side comparison of the two standards to help clarify the differences:
| Feature | IEC 62040-1 | UL 1778 |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Market | International (Europe, Asia, etc.) | North America (U.S. and Canada) |
| U.S. Market Access | Recognized but often insufficient for local codes | Essential for U.S. installation and regulatory approval |
| Cost Factor | $440–$770 USD | Requires separate UL testing and listing fees |
| Global Market Access | Facilitates global trade and export | Mandatory for North American fire and safety codes |
| Design Focus | Electrical, mechanical, and thermal safety | Fire safety, insulation, and energy efficiency |
| Certification Scope | Broad global recognition | Limited recognition outside North America |
These differences are crucial when aligning your project with regional and safety requirements.
For installations in the U.S., UL 1778 certification is a must. It ensures that your UPS system complies with local building codes and insurance requirements, which IEC 62040-1 alone cannot fully satisfy. Many manufacturers now opt for dual certification to avoid costly redesigns when entering markets with different standards. This strategy allows them to maintain a unified product line while meeting both North American and international requirements.
If you're sourcing equipment from trusted suppliers like Electrical Trader, always check the certifications carried by the UPS system. For U.S.-based projects, prioritizing UL 1778 compliance can save you from potential delays and regulatory headaches.
While IEC 62040-1 certification costs range from $440 to $770 USD, UL 1778 involves additional testing and listing fees. However, investing in properly certified equipment can save money in the long run by reducing risks associated with product failures, liability issues, and inefficiencies. This comparison underscores the importance of selecting certifications that align with the regional codes relevant to your project.
Conclusion
Where you install your UPS system directly impacts the safety standards you need to meet. In the United States and Canada, UL 1778 certification is a must. This certification ensures the system complies with North American fire safety codes, electrical insulation standards, and local building regulations. Without it, you could face installation delays or even regulatory penalties.
For installations in Europe, Asia, or other international markets, IEC 62040-1 is the go-to standard. It focuses on electrical, mechanical, and thermal safety requirements and has been updated since 2017 to align with IEC 62477-1, which addresses power electronic converter systems. Its broad international recognition makes it ideal for global operations. This difference underscores the importance of aligning certifications with local requirements.
If your facility spans multiple regions, consider using dual-certified equipment to simplify compliance. Make sure any UPS systems you purchase - like those available from Electrical Trader - carry the appropriate certifications for your specific environment.
FAQs
Why is dual certification important for UPS systems?
Dual certification means that an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) meets both IEC 62040-1 international safety standards and UL 1778, which is tailored specifically to North America. This ensures the UPS adheres to strict safety guidelines, addressing fire hazards, electrical safety, and performance efficiency.
It also makes the UPS eligible for use in both global markets and the U.S./Canada, providing flexibility for various applications across different regions.
What is the difference between IEC 62040-1 and UL 1778 standards for UPS systems?
The IEC 62040-1 standard serves as a globally recognized guideline, detailing the safety requirements for uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems. It covers electrical, mechanical, and thermal safety to ensure these systems operate reliably and securely across various international markets.
On the other hand, UL 1778 is a standard designed specifically for North America, addressing UPS systems used in the United States and Canada. It goes beyond the basics by including additional requirements for fire safety, insulation, and energy efficiency. Compliance with UL 1778 is mandatory for UPS equipment sold or installed in these regions.
Although both standards prioritize safety, their focus differs. IEC 62040-1 provides a comprehensive international framework, while UL 1778 caters to the unique needs of North American markets.
What thermal safety measures does IEC 62040-1 require for UPS systems?
The IEC 62040-1 standard sets clear and stringent rules to ensure the thermal safety of uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems. These guidelines focus on controlling temperature increases, avoiding overheating, and reducing the risk of fire. Importantly, they are designed to protect everyone involved - whether it's general users or trained technicians - against potential thermal hazards during installation, operation, or maintenance.
By following these safety measures, UPS systems can deliver dependable backup power while maintaining safe operation across a variety of conditions.
