
Generator Maintenance Schedule Guide
Share
Skipping generator maintenance can cost you thousands and lead to failures during critical moments. Regular upkeep ensures reliability, extends lifespan, and reduces repair costs. Here's what you need to know:
- Reliability Boost: Proper maintenance increases emergency reliability to 94%, compared to 67% for neglected units.
- Cost Savings: Preventive care costs $3,000–$5,000 annually, while emergency repairs can hit $15,000–$40,000. Downtime in critical facilities can exceed $100,000.
- Common Failures: 23% of generator failures are due to preventable issues like missed oil changes or corroded batteries.
- Lifespan: Maintenance can extend a generator's life to 20+ years.
Key Maintenance Steps:
- Follow OEM guidelines for oil, filter, and component checks based on runtime hours or calendar schedules.
- Adjust frequency for extreme conditions (e.g., high heat, cold, or dust).
- Perform weekly visual checks, monthly load tests, and annual professional servicing.
- Keep detailed service logs to maintain warranties and track performance.
Load Testing:
- Prevents issues like carbon buildup.
- Confirms generator performance under real conditions.
- Required for compliance with standards like NFPA 110.
Pro Tip: Use platforms like Electrical Trader to source parts efficiently, ensuring your generator stays operational.
Regular maintenance not only protects your investment but also ensures your generator is ready when you need it most.
How To Perform Annual Schedule A Maintenance Generac 20kw Automatic Whole House Standby Generator
sbb-itb-501186b
OEM Guidelines and Custom Maintenance Schedules
The manufacturer's manual is your go-to resource for creating a maintenance plan. Most OEM guidelines follow a dual-tracking approach, using either calendar time (e.g., every two years) or operating hours (e.g., every 200 hours), whichever comes first. This system ensures proper care for generators, whether they sit idle for long periods or run frequently during power outages.
Don’t skip the break-in period. For new generators, the first oil and filter change is critical and should happen after just 20 to 25 hours of runtime. This step removes any particles from the assembly process that could harm the engine, setting your generator up for long-term reliability. Neglecting this early maintenance can lead to unnecessary engine wear.
OEM schedules are designed for moderate conditions, typically temperatures between 40°F and 85°F (4.4°C to 29.4°C). If your generator operates in more extreme environments, you’ll need to double the frequency of oil and filter changes. For example, instead of every 200 hours or two years, switch to every 100 hours or annually. Dusty areas, high humidity, or exposure to coastal salt air also require more frequent air filter checks and component inspections.
Your generator's usage patterns also play a big role in maintenance. For example, during multi-day outages, generators running continuously should be checked daily for oil levels and leaks. Facilities classified under NFPA 110 Level 1, such as hospitals or emergency lighting systems, have stricter requirements. These include weekly test runs and monthly load tests lasting at least 30 minutes at 30% or more of the generator’s rated load.
To keep track of runtime, use the hour meter on the control panel or a remote monitoring app. Hour-based tracking is more precise than relying on calendar dates alone [1,10]. Maintaining detailed service records is equally important, as they may be required to keep your warranty valid. Opting for OEM-specific maintenance kits, which include the correct oil, filters, and spark plugs, ensures all parts meet the manufacturer’s standards.
| Service Task | Standard Conditions | Extreme Conditions (<40°F or >85°F) |
|---|---|---|
| Oil & Filter Change | Every 200 hours or 2 years | Every 100 hours or 1 year |
| Air Filter Inspection | Every 100 hours or 1 year | More frequent (based on dust/debris) |
| Valve Clearance | Every 2–4 years (if applicable) | After first 25 hours, then per OEM advice |
| Continuous Run Checks | N/A | Daily (every 24 hours) |
Maintenance Checklists by Frequency
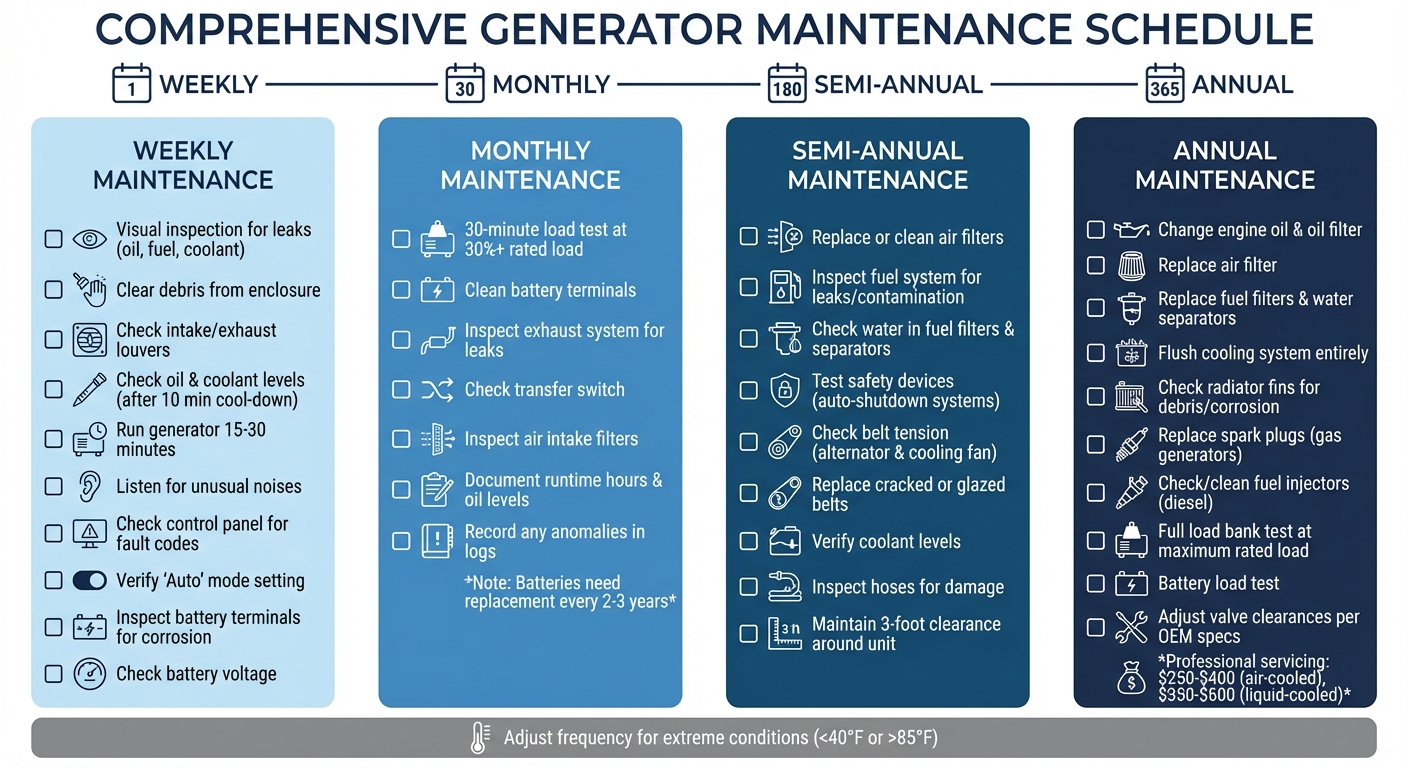
Generator Maintenance Schedule: Weekly, Monthly, Semi-Annual & Annual Tasks Checklist
Breaking down maintenance tasks into specific time intervals ensures your generator stays in top condition without overwhelming your schedule. Each frequency level focuses on components based on their wear and tear patterns. Skipping even minor tasks can lead to major failures when you need the generator most. Regular attention to these tasks helps maintain reliability and prepares your generator for critical loads.
Weekly Maintenance Tasks
Weekly maintenance revolves around quick visual checks and ensuring operational readiness. Begin by inspecting the entire unit for any oil, fuel, or coolant leaks. Clear away any debris around the generator's enclosure to prevent blockages. Examine the intake and exhaust louvers for obstructions, and after allowing the generator to cool for about 10 minutes, check oil and coolant levels.
Run the generator for 15 to 30 minutes to confirm it starts and operates smoothly. While it's running, listen for any unusual noises like grinding or knocking, and keep an eye out for excessive smoke or power fluctuations. Check the control panel for fault codes and ensure the generator is set to "Auto" mode so it’s ready for emergencies. Don’t forget to inspect battery terminals for corrosion and verify voltage readings.
"A gas or diesel generator isn't a 'set it and forget it' type of device. It pays to conduct a visual inspection of the generator before every use, and create a maintenance schedule that includes weekly, monthly, and annual checkups" - Dustin Eusebio from BigRentz.
These weekly tasks lay the groundwork for more in-depth monthly maintenance.
Monthly Maintenance Tasks
Monthly maintenance goes beyond visual checks, focusing on functional performance. Run a 30-minute load test at 30% or higher of the generator's rated load instead of just letting it idle. This prevents "wet stacking", a condition where carbon builds up in diesel engines running at low loads. Clean the battery terminals thoroughly to remove any corrosion, and keep in mind that batteries typically need replacing every 2 to 3 years, as battery failure is a leading cause of generator start issues.
Inspect the exhaust system, including the muffler and exhaust pipes, for leaks or signs of overheating that could damage nearby components. Check the transfer switch and air intake filters for wear or contamination. Lastly, document runtime hours, oil levels, and any anomalies in detailed logs. These records are crucial for spotting trends, planning future maintenance, and staying compliant with warranty requirements.
Semi-Annual Maintenance Tasks
Every six months, it’s time to tackle potential issues that might not show up during weekly or monthly checks. Start by replacing or cleaning air filters, especially if your generator operates in a dusty environment. Inspect the fuel system for leaks, contamination, or water in the filters and separators. Test all safety devices, such as automatic shutdown systems for low oil pressure or high temperature, to ensure they’re working properly.
Check the tension and condition of belts on the alternator and cooling fan, replacing any that are cracked or glazed. Verify coolant levels and inspect hoses for soft spots or brittleness. Keep at least a 3-foot clearance around the unit, and promptly clear away leaves, grass, or snow to prevent overheating or intake blockages.
Annual Maintenance Tasks
Annual maintenance involves a comprehensive inspection and typically requires professional servicing. This includes changing the engine oil and oil filter, replacing the air filter, and swapping out fuel filters and water separators. Flush the cooling system entirely and check radiator fins for debris or corrosion. For gas generators, replace the spark plugs, while diesel models should have their fuel injectors checked and cleaned.
Conduct a full load bank test at maximum rated load to remove carbon buildup and confirm the generator operates at peak performance. Perform a battery load test to ensure it has enough cranking power, especially in colder climates. Adjust valve clearances according to the manufacturer’s specifications to maintain proper engine timing and fuel efficiency.
Professional servicing costs can vary: air-cooled generators typically range from $250 to $400, while liquid-cooled units cost between $350 and $600. Schedule these annual services strategically - plan for May or June in hurricane-prone areas and September or October in regions that face winter storms.
Next, we’ll dive into load testing procedures to evaluate overall generator performance.
Load Testing Procedures
Load testing involves applying incremental loads - 25%, 50%, 75%, and 100% - to ensure the generator performs as expected. This step-by-step process gradually increases the load until the generator reaches full operating temperature. It helps identify hidden issues like voltage instability, overheating, or fuel system leaks that might not show up during no-load operation.
Regular high-load testing also plays a key role in preventing wet stacking. For facilities where uninterrupted operation is critical, standards like NFPA 110 and the Joint Commission mandate specific testing routines. These include a monthly 30-minute test at 30% load and a full 4-hour test at maximum load every 36 months. For non-critical facilities, an annual test at 80% of the maximum load for at least 60 minutes is recommended to reduce the risk of unexpected failures.
"Load testing verifies real performance under kW and thermal stress and exposes control or cooling issues you won't see at idle." - ABM
During testing, it's essential to record key parameters such as voltage, frequency, oil pressure, coolant temperature, and exhaust conditions. Pay attention to how well the voltage and frequency recover during rapid load changes, ensuring they stabilize without excessive fluctuation.
Pre-Test Checklist:
- Implement lockout/tagout procedures.
- Verify proper cooling airflow.
- Ensure fire extinguishers are on hand.
Post-Test Steps:
- Run the generator under light or no-load conditions for 5 to 10 minutes before shutting it down.
- Inspect for leaks, loose connections, or signs of thermal stress.
These steps not only ensure safety but also provide valuable data for assessing the generator's performance under real-world conditions. They also help differentiate the behavior of resistive and reactive load banks.
When selecting a load bank, it's crucial to match it to your facility's electrical needs. Resistive load banks simulate linear loads like lighting and heaters, operating at a unity power factor. Reactive load banks, on the other hand, mimic inductive loads such as motors and transformers, operating at a 0.8 power factor. Choosing the right type ensures accurate performance data that aligns with your facility's actual electrical demands.
Finding Parts and Equipment on Electrical Trader
Keeping generators running smoothly requires more than just regular maintenance - it also depends on finding the right parts when you need them. Electrical Trader offers a marketplace where you can source new, used, and surplus electrical equipment from top brands like Siemens, ABB, GE, and Generac. Products are conveniently organized into categories such as Power Generation, Breakers & Components, Transformers, and Low/Medium/High Voltage equipment, making it simple to track down the exact parts you need. Choosing the right components is key to extending your generator's lifespan and staying on top of maintenance schedules.
The platform’s filters let you search by voltage, capacity, and category, which is especially useful for locating compatible parts for older generators where OEM options might no longer be available. Beyond basic items like oil, fuel, and air filters, Electrical Trader also supplies specialized components, including starter motors, automatic voltage regulators (AVRs), relays, sensors, and battery chargers - perfect for tackling more complex repairs.
Pricing is flexible, with options ranging from premium to budget-friendly components, allowing facilities to manage costs without compromising on quality.
"Our platform helps you find exactly what you need by voltage, capacity, and category, while ensuring quality and competitive pricing." – Electrical Trader
For facilities juggling multiple generator units or dealing with supply chain challenges, having a dependable source for critical parts is crucial. Electrical Trader simplifies the process, helping you keep maintenance projects on track and ensuring your generators stay operational for the long haul.
Conclusion
Regular maintenance is the cornerstone of extending your generator's lifespan - potentially by two to three times - and keeping repair costs in check. Annual upkeep, typically costing between $250 and $400, is far less expensive than emergency repairs, which can range from $1,000 to $2,000 or more. Plus, it ensures your generator is ready to kick in when you need it most, a critical safeguard no facility can overlook during outages.
To get the most out of your generator, align your maintenance schedule with OEM recommendations and adjust for local conditions, such as extreme heat or cold, which may necessitate more frequent oil and filter changes. Monthly load testing at 30% capacity helps prevent issues like wet stacking and carbon buildup. Keeping detailed records not only supports warranty claims but also ensures compliance with standards like NFPA 110.
"A well-maintained generator can mean the difference between constant power and unexpected failures." – Woodstock Power
Using high-quality parts, such as those available from Electrical Trader, plays a big role in keeping your generator in top shape. With proper preventive care and the right components, you can achieve up to 98.5% reliability and extend the equipment's lifespan to 25 years or more.
A disciplined, well-planned maintenance routine is your best defense against downtime. It protects your investment, minimizes unexpected failures, and ensures your generator is ready to perform when power outages strike. In the end, a combination of precise scheduling and premium parts guarantees the reliability you need when it matters most.
FAQs
How do I choose between hour-based and calendar-based maintenance?
When deciding on a maintenance schedule for your generator, it often comes down to how and where it's used. Hour-based maintenance works best for generators that run frequently or under heavy loads, as it tracks runtime to address wear and tear. On the other hand, calendar-based maintenance is better suited for backup generators or those used infrequently, ensuring key components like batteries and filters are inspected on a regular timeline. Many owners opt for a combination approach, such as servicing every 200 hours of use or every two years - whichever happens first.
What load test do I need for my facility type?
The type of load test you need will vary based on your facility's power requirements and operational needs. In most cases, a load bank test that replicates the generator's full rated load is suggested. This approach helps verify the generator's performance under conditions it would face during actual use, ensuring it operates reliably and as intended.
What parts should I keep in stock for quick repairs?
To keep things running smoothly, it's smart to have essential parts like oil filters, fuel filters, spark plugs, and batteries readily available. Having these frequently replaced components on hand means you can handle quick repairs without unnecessary delays, keeping downtime to a minimum.
