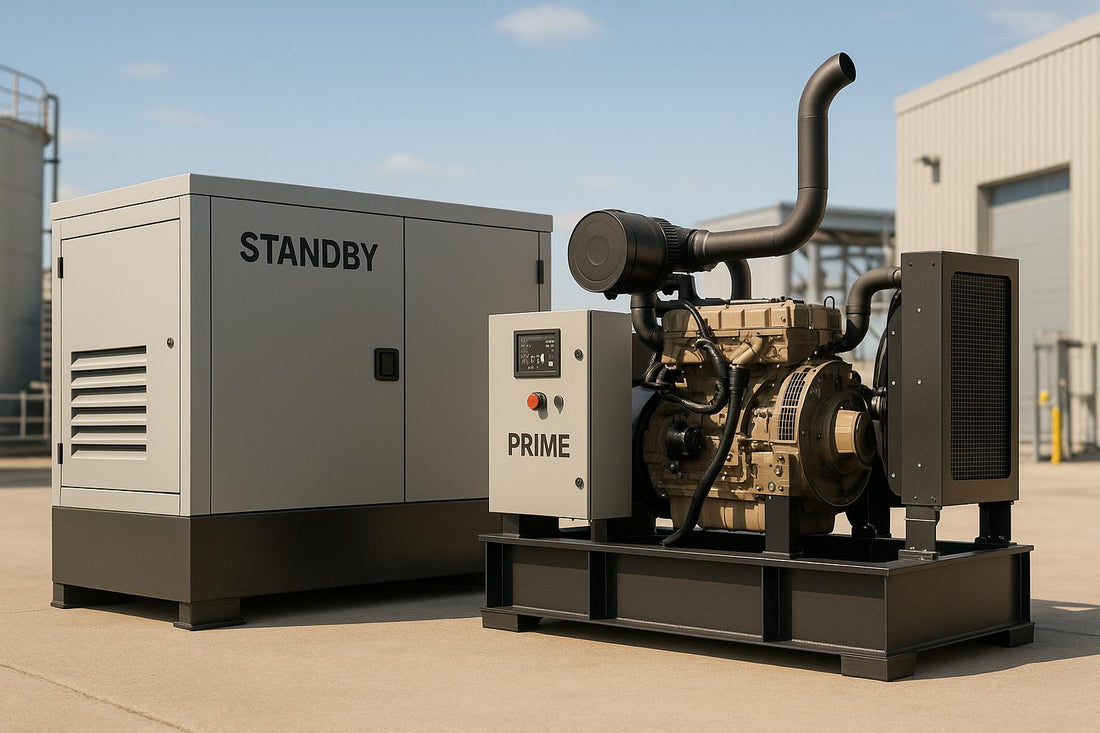

Ultimate Guide to Standby and Prime Generators
Share
Need reliable power? Whether for emergencies or continuous use, choosing the right generator is crucial. Here's what you need to know:
- Standby Generators: Backup power for emergencies, designed for short-term use (up to 200 hours/year). Ideal for homes, hospitals, and businesses during outages.
- Prime Generators: Built for continuous use as the main power source, handling variable loads. Perfect for construction sites, remote operations, or areas without grid access.
-
Key Differences:
- Run Time: Standby is limited; prime can run 24/7.
- Durability: Prime is more robust but requires frequent maintenance.
- Cost: Prime has higher upfront costs; standby is more affordable for occasional use.
Quick Comparison
| Feature | Standby Generator | Prime Generator |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Emergency backup | Continuous power source |
| Run Time | Limited (200 hours/year) | Unlimited (24/7 operation) |
| Ideal For | Outages in urban areas | Remote or off-grid locations |
| Maintenance | Less frequent | More frequent |
| Cost | Lower | Higher upfront investment |
Pro Tip: Choose standby generators for infrequent outages and prime generators for continuous or heavy-duty use. Proper sizing, fuel type, and maintenance are essential for reliability and efficiency.
What is diesel generator prime power rating and standby power rating
Key Differences Between Standby and Prime Generators
Choosing the right generator depends on how you plan to use it. Standby and prime generators are built for different purposes, and these differences affect their performance, durability, and cost over time.
Feature and Use Case Comparison
Standby and prime generators differ significantly in their design and operational capabilities. Here's a breakdown of their key features:
| Feature | Prime Power | Standby Power |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Main power source | Backup power source |
| Generator Load | Variable | Variable or constant |
| Run Time | Unlimited | Limited (around 1 hour per 12-hour cycle) |
| Ideal For | Areas without grid access | Emergencies during power outages |
| kVA Rating | Typically lower | Typically higher |
| Warranty | Usually shorter | Usually longer |
Prime generators are engineered for continuous use, with durable engines and enhanced cooling systems. As long as the load stays between 50% and 100% of the generator's prime rating, they can run indefinitely. They can also handle a 10% overload for up to an hour in a 12-hour period, though this is capped at 500 hours annually.
Standby generators, on the other hand, are designed for shorter, infrequent use - up to about 200 hours per year. Pushing them beyond this limit can lead to mechanical failures and a shorter lifespan.
According to ISO-8528-1 standards, prime generators should maintain a 24-hour average load factor of no more than 70% of their nameplate PRP rating to ensure long-term reliability and efficiency.
These differences influence how various industries deploy these generators.
Common Applications in U.S. Industries
Standby and prime generators excel in different scenarios, and their use often depends on the specific needs of an industry.
Standby generators are the go-to choice for critical backup power. They’re widely used in industries where maintaining operations during a power outage is essential. For example, commercial and industrial facilities depend on standby generators to keep air conditioning, heating, computer systems, and security systems functional during outages. Emergency services like police and fire stations, as well as telecommunications companies, also rely heavily on these generators.
"Standby commercial generators used as a backup power solution not only keep the lights on, but can also maintain safe working environments for you and your employees." - Woodstock Power Company
Prime generators, by contrast, are indispensable in locations without reliable grid access. Construction sites often use them to power tools, machinery, and lighting, especially for night work or underground projects. Mining operations depend on prime generators for drilling equipment, shovels, and tunnel lighting.
In agriculture, prime generators are critical for running lights, heaters, fans, and other equipment. Dairy farms, in particular, rely on them to maintain proper milk storage temperatures and support animal care. Manufacturing plants also use prime generators to power machinery essential for production.
As of 2022, the global generator market was valued at around $20 billion and is projected to grow to $27 billion by 2027, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.2%. Prime generators account for roughly 40% of the market, driven by industrial demand, while standby generators dominate the residential and commercial sectors, holding about 60% of the market share.
Understanding these applications highlights the strengths and limitations of each type, as detailed below.
Pros and Cons of Each Type
Both prime and standby generators have their own set of advantages and drawbacks, depending on your needs and budget.
Prime Generator Pros:
- Built for continuous, long-term use.
- Can handle variable loads and occasional overloads.
- Designed with heavy-duty components for reliability under tough conditions.
Prime Generator Cons:
- Higher upfront costs due to more durable components.
- Shorter warranty periods, reflecting their intensive usage.
- Require frequent maintenance, which can increase operational costs over time.
Standby Generator Pros:
- Longer warranty periods since they’re used less frequently.
- Offer higher kVA ratings relative to their size, ideal for emergency power needs.
- Require less frequent maintenance, making them easier to manage.
Standby Generator Cons:
- Not designed for continuous operation; overuse can lead to breakdowns.
- Need regular testing to ensure they’re ready for emergencies.
- Less flexibility compared to prime generators.
Ultimately, the choice between a standby and a prime generator comes down to your specific power needs. Whether you require backup power for emergencies or a primary power source for continuous use, understanding these differences will help you invest in the right generator for your situation.
Important Features and Specifications
When it comes to choosing the right generator, understanding its technical specs is key. These features can determine whether your generator runs smoothly or becomes a source of frustration and downtime.
Power Output and Performance
The power rating of a generator is one of its most important aspects. You'll often see two types of ratings: prime power and standby power, each suited for different scenarios.
- Prime generators are built for continuous use, typically running at 70–80% capacity. They can handle a brief 10% overload, making them a great choice when power demands fluctuate unexpectedly. These units generally last between 15,000 and 20,000 hours.
- Standby generators, on the other hand, are designed to kick in during grid outages, operating at full capacity until utility power is restored. Their lifespan is shorter, averaging 2,500 to 3,000 hours.
Fuel consumption also differs between the two. Prime generators use about 0.25 to 0.35 liters of fuel per kWh (approximately 0.07 to 0.09 gallons per kWh), while standby units consume slightly more, around 0.28 to 0.40 liters per kWh (roughly 0.07 to 0.11 gallons per kWh). This reflects the balance between efficiency for continuous use and the surge capacity needed for emergencies.
Another key factor in generator performance is the type of fuel it uses.
Fuel Types and Storage Requirements
The choice of fuel directly impacts operating costs, convenience, and environmental impact. Diesel and natural gas are the most common options, each with its own set of advantages.
Diesel Generators
Diesel generators are known for their efficiency, particularly during high loads or sudden load changes. Diesel fuel delivers about 129 BTUs per unit, far more than natural gas's 37 BTUs, ensuring reliable performance when demand spikes. Diesel's efficiency also extends to remote or off-grid applications since these generators rely on on-site fuel storage. With proper treatment, diesel fuel can be stored for up to a year, though untreated fuel typically lasts 6–12 months.
However, diesel isn't without its drawbacks. Fuel costs are higher, and storage requires careful management to prevent spoilage. Diesel generators are also louder and produce more emissions compared to natural gas units.
Natural Gas Generators
Natural gas is a great option for urban settings with easy access to utility hookups. These generators connect directly to the gas line, eliminating the need for on-site storage and providing an almost unlimited fuel supply. Natural gas also burns cleaner, emitting about 116.65 pounds of CO₂ per million BTUs compared to diesel's 163.45 pounds. It produces significantly less carbon dioxide than coal or oil, making it a more environmentally friendly choice.
That said, natural gas generators come with higher upfront costs and require more maintenance. They also have a larger physical footprint, which might be a consideration for space-constrained installations.
Here’s a quick comparison:
| Generator Fuel Source | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Diesel | Efficient under heavy loads Easier maintenance Long lifespan Works well in remote areas On-site fuel storage ensures independence |
Higher fuel costs Requires careful fuel management Noisy Produces more emissions |
| Natural Gas | Lower fuel costs Unlimited fuel supply via utility hookup Quieter operation Cleaner emissions Ideal for urban areas |
Higher initial investment More complex maintenance Larger physical size Requires connection to a utility line |
Diesel units tend to have simpler internal components, which means less maintenance overall. They are also safer to operate, as diesel fuel is less flammable than natural gas.
Beyond fuel type, modern generators come with advanced control systems that enhance efficiency and reliability.
Control Systems and Automation
Today's generators are packed with technology to make operation easier and more efficient. These control systems handle tasks automatically, reducing the need for constant supervision and minimizing the risk of costly failures.
- Automatic transfer switches and load management systems ensure seamless operation during outages. These systems balance power loads in real-time, protect critical circuits, and manage cool-down periods when utility power is restored.
- Remote monitoring allows operators to check fuel levels, maintenance schedules, and overall system status from anywhere. Alerts can be sent via email or text to flag potential issues before they escalate.
- Programmable maintenance reminders track operating hours, fuel usage, and service intervals. This ensures routine tasks like oil changes and filter replacements are never overlooked, keeping the generator running smoothly.
For large-scale operations, paralleling controls allow multiple generators to work together. These systems distribute power loads across units and provide redundancy - if one generator fails, others can take over to maintain uninterrupted power.
Control systems range from basic models with simple start/stop functions to industrial-grade units offering detailed monitoring, data logging, and integration with building management systems. This added sophistication helps ensure reliability and efficiency, even in demanding applications.
sbb-itb-501186b
How to Choose the Right Generator for Your Application
Selecting the right generator involves more than just understanding power metrics. It requires a thorough evaluation of your power needs, operating conditions, and budget. Picking the wrong generator can lead to inefficiencies, costly breakdowns, and even damage to your equipment.
Calculating Power Needs and Load Profiles
The first step in choosing a generator is figuring out how much power you actually need. This isn't as simple as adding up the wattage ratings on your devices. You also need to factor in both running and starting power requirements. For example, devices like compressors or motors often draw significantly more power when starting up - sometimes up to six times their running load.
Here’s a quick example: A refrigerator with a running wattage of 350 watts might need around 1,400 watts to start (350 watts running + 350 × 3 for startup).
| Common Appliances | Running Watts |
|---|---|
| Refrigerator or Freezer | 150 |
| Microwave Oven | 1,000 |
| Dishwasher | 1,250 |
| Coffee Maker | 1,000 |
| Electric Range | 1,200 |
| Washing Machine | 800 |
| Gas Clothes Dryer | 1,800 |
| Electric Clothes Dryer | 3,000 |
| Window AC (10,000 BTU) | 900 |
| Window AC (12,000 BTU) | 3,250 |
For commercial spaces, a useful guideline is 50 kW plus an additional 10 watts per square foot for retail environments, or 50 kW plus 5 watts per square foot for other commercial applications. Proper sizing is crucial - oversized generators can strain your electrical system and waste resources, while undersized ones may overheat or fail to meet your power demands. To be safe, consider adding about 25% extra capacity to accommodate unexpected surges or future expansions.
Additional factors like single-phase vs. three-phase power and compliance with NEC requirements should also be considered. If you're unsure, consulting a certified electrician is a smart move.
Runtime and Duty Cycle Considerations
How long and how often you plan to use your generator plays a big role in determining the right type. This impacts not only the purchase price but also ongoing fuel and maintenance costs.
- Standby Generators: Designed for emergencies, these are built for short bursts of use - typically no more than 1 hour in a 12-hour period. They often have higher kVA ratings but shorter warranties since they aren’t meant for continuous operation.
- Prime Power Generators: Built for heavy-duty, long-term use, these can run for unlimited hours. They handle variable loads and typically operate between 50% and 100% of their prime rating. While they have lower kVA ratings compared to standby units, they’re ideal for situations like remote worksites or areas with frequent power outages.
For constant power needs, continuous generators are the go-to choice. For instance, MTU Onsite Energy offers ESP-rated generators approved for an 85% 24-hour average load factor, while PRP-rated sets are approved for a 75% 24-hour average load factor. Overusing a standby generator for long durations can lead to breakdowns and reduced lifespan.
Budget and Maintenance Factors
The type of generator you choose also affects your overall costs, from the initial purchase to long-term expenses like fuel and maintenance.
Initial Costs
Prime power generators start at around $20,000 for a 44 kVA unit and can climb to $100,000 for a 500 kVA model. Standby generators, depending on size, range from about $9,000 for smaller units to over $200,000 for larger ones. If you deal with frequent outages, the higher upfront cost of a prime or continuous generator may be justified.
Maintenance Requirements
Maintenance schedules vary by generator type and usage. Portable units may need servicing every 50–100 hours, while diesel generators typically require maintenance every 250–500 hours. Regular upkeep is essential for ensuring reliability and extending the generator's lifespan - some units can last up to 25 years with proper care.
"You want to maximize the life of your generator and make the most of your investment. Ongoing, regular maintenance helps you get your money's worth." – H.O. Penn
Key maintenance tasks include oil and filter changes, air filter cleaning, spark plug checks, monthly battery and coolant inspections, and annual load bank testing.
Fuel Options
Your choice of fuel impacts both running costs and convenience. Gasoline is often the cheapest and easiest to find, while propane burns cleaner. Diesel, though more expensive, is efficient for heavy use, and natural gas offers the convenience of a continuous supply through existing pipelines.
For smooth operation, standby generators often require a transfer switch to handle transitions during outages. To avoid overloading, choose a generator with at least 30% more capacity than your total calculated load. This ensures reliable performance and prevents damage during startup surges.
Finding Generators Through Trusted Marketplaces
Once you’ve figured out your power needs and set a budget, the next step is finding a dependable place to buy your generator. Traditional methods like visiting dealers or scouring classified ads can be time-consuming and limit your choices. Online marketplaces have changed the game, providing access to both new and used generators from verified sellers across the U.S. Among these platforms, Electrical Trader stands out for its user-friendly approach and focus on quality equipment.
Overview of Electrical Trader
Electrical Trader is a dedicated online marketplace specializing in electrical components and power distribution equipment, including both standby and prime generators. It caters to electricians, contractors, and anyone needing reliable power solutions. The platform offers a wide selection of products from trusted names like Kohler, Cummins, and John Deere. Whether you’re looking for a compact residential backup generator or a heavy-duty industrial unit, each listing includes detailed specs, manufacturer details, and high-quality images to help you make an informed decision.
By partnering with reputable sellers, Electrical Trader minimizes the risks tied to unverified sources - such as incomplete maintenance records or unknown equipment history. This makes it easier to confidently purchase the right generator, building on the selection tips covered earlier.
How to Navigate Product Categories
Electrical Trader organizes its inventory into straightforward categories, making it simple to find what you need. The platform’s search and filter tools allow you to sort listings by factors like power output, fuel type (diesel, natural gas, or propane), application (standby or prime), and manufacturer.
When browsing, pay close attention to key details like the odometer reading (total operational hours) and the manufacture year. Newer models are often more efficient and more likely to meet current EPA standards. The platform offers both new generators, which often include full manufacturer warranties, and used options that can provide significant cost savings. This structure helps streamline your search and ensures you’re focusing on the best choices for your needs.
Benefits of Using a Centralized Marketplace
Electrical Trader simplifies the buying process for businesses by centralizing orders, inquiries, and bids, offering several key advantages:
Cost Savings and Efficiency
Online platforms like Electrical Trader can lead to significant savings. According to a 1999 Deloitte Consulting survey, companies that adopted e-procurement saved between 5% and 15% on overall spending, with over 40% of participants reporting savings above 10%. These reductions are largely due to the elimination of outdated, paper-based supply-chain processes.
Access and Convenience
The platform connects buyers to a broad range of generators from various manufacturers, helping you quickly find options that meet your specific criteria. Listings include detailed datasheets and specifications, making it easy to compare products and make informed decisions.
Quality Assurance
Unlike general auction sites, Electrical Trader prioritizes quality. Sellers on the platform often offer competitive prices without cutting corners on reliability. Many also provide technical support to help buyers select the right equipment. When reviewing listings, focus on factors like the manufacturer’s reputation, the generator’s age and condition (check the odometer reading and manufacture year), fuel type compatibility, and available warranties. The ability to compare multiple options side-by-side ensures you’ll find the best fit for your budget and application.
Conclusion: Making a Smart Generator Purchase
Choosing the right generator is all about identifying your specific power needs and pairing them with the right type of equipment. Standby generators are perfect for automatic backup power during outages, operating for limited periods. On the other hand, prime generators are designed for continuous use, making them ideal for remote locations or operations with fluctuating power demands. Understanding this distinction is key to making a practical and cost-efficient choice.
Keep in mind, your decision impacts more than just the upfront cost. Maintenance plays a major role in long-term reliability - over 70% of generator failures are linked to poor upkeep. Prime generators, while capable of running continuously, often come with shorter warranties. In contrast, standby units typically offer longer warranty periods but include specific usage limitations.
When assessing your power needs, think both short-term and long-term. Misjudging your requirements - whether by overestimating or underestimating - could lead to equipment failure or insufficient power during critical situations.
Another important factor is where you buy your generator. A trusted marketplace like Electrical Trader, which specializes in electrical components and power distribution equipment, connects you with knowledgeable sellers. Pay attention to details like the manufacturer's reputation, the year of manufacture, and the warranty terms when reviewing listings.
Generators differ in fuel types, runtime capabilities, and control features, so your choice should be tailored to your operational needs. Whether you're looking for a small residential backup generator or a heavy-duty industrial system, focus on your specific power requirements, budget, and ability to maintain the equipment. This thoughtful approach ensures you’ll invest in a generator that meets your needs reliably for the long haul.
FAQs
What should I consider when choosing between a standby and a prime generator?
When choosing between a standby generator and a prime generator, it all comes down to how you plan to use it. Standby generators are designed to kick in during power outages, running for only a few hours or days each year. They’re a great fit for homes or businesses that need power during emergencies but don’t rely on generators for daily operations.
Prime generators, however, are built for the long haul. They’re meant to be a primary power source, running continuously in places where utility power is unreliable or unavailable. If you need a generator to handle ongoing, variable power demands, a prime unit is the way to go.
It’s also important to think about your specific power requirements. Prime generators can handle fluctuating loads over extended periods, while standby generators are optimized for short-term, maximum output. Keep in mind that prime generators often need larger fuel tanks and more frequent maintenance due to their continuous use. Standby generators, on the other hand, are easier to maintain since they run less often. Weighing these factors will help you decide which type of generator best suits your needs.
How does the type of fuel affect a generator's performance and cost-efficiency?
The type of fuel you select significantly impacts your generator's performance and overall operating costs. Diesel generators are known for their efficiency, delivering more power per gallon than many other fuel types. This makes them a great choice for heavy-duty tasks. On the flip side, diesel fuel often comes with a higher price tag and may lead to extra maintenance needs due to emissions and the complexity of diesel engines.
If you're looking for a cleaner option, natural gas and propane generators might be the way to go. These fuels burn more cleanly, resulting in lower emissions, which can be a plus for those mindful of environmental concerns. While they might not pack quite the same energy punch as diesel, they can be a more economical choice in areas where natural gas or propane is readily accessible. To choose the right generator, weigh factors like fuel availability, running costs, and the specific power demands of your situation.
What are the key maintenance steps to keep standby and prime generators running reliably?
To keep your standby and prime generators in top shape, regular maintenance is a must. Start with basic inspections - check oil levels, look over the fuel system for any signs of leaks, and make sure all battery connections are clean and securely attached. Stick to the manufacturer's maintenance schedule, which typically includes tasks like changing oil and filters, testing the cooling system, and running load tests to ensure the generator operates as it should under real-world conditions.
Even if your generator isn’t used often, it’s a good idea to run it periodically. This prevents problems like fuel breakdown and battery drain while also keeping the system properly lubricated. Keeping a detailed maintenance log is another smart move. It helps you track service history, identify recurring issues, and ultimately ensures the generator remains reliable for the long haul.
Related posts
- Top 5 Power Generation Tools for 2025
- 10 Best Circuit Breakers for Industrial Use
- Voltage Regulation Problems: Causes and Fixes
- How Urban Growth Impacts Power Distribution Systems
