
Ultimate Guide to Portable Power Stations for Outdoor Use
Share
Portable power stations are rechargeable batteries that provide electricity on the go, making them ideal for camping, RV trips, or even home backup. They power devices like phones, laptops, portable fridges, and medical equipment without noise or fumes. Modern models use long-lasting LiFePO4 batteries, support various charging methods (AC, car, solar), and offer multiple output ports (AC, USB, 12V). Here's what you need to know:
- Battery Capacity: Measured in watt-hours (Wh), it determines how long devices can run. For example, a 1,000Wh station can power a 60W laptop for over 16 hours.
- Power Output: Includes continuous power (for steady use) and surge power (for device startup). Pure sine wave inverters are best for sensitive electronics.
- Sizes: From compact (under 300Wh) for day trips to high-capacity (over 2,500Wh) for RVs or home backup.
- Charging Options: AC wall outlets, car adapters, and solar panels. Solar is great for off-grid use, and MPPT controllers improve efficiency.
- Durability: Look for rugged designs and weather resistance (e.g., IP67 ratings) for outdoor use.
Top Picks:
- Anker Solix C1000 Gen 2: 1,056Wh, recharges in 49 minutes, ~$400–$450.
- Jackery Explorer 300 Plus: Lightweight (8.27 lbs), 288Wh, ~$349.
- EcoFlow Delta Pro 3: 4,096Wh, expandable, ~$2,699–$3,699.
Maintenance Tips:
- Keep batteries between 20–80% charge.
- Store at 50–60% charge in cool, dry conditions.
- Avoid water exposure and extreme temperatures.
Portable power stations are a quiet, clean energy solution for outdoor adventures and emergencies. By selecting the right capacity and maintaining it properly, you can ensure reliable performance for years.
How to Pick The RIGHT Portable Power Station (For Beginners)
sbb-itb-501186b
Features and Types of Portable Power Stations
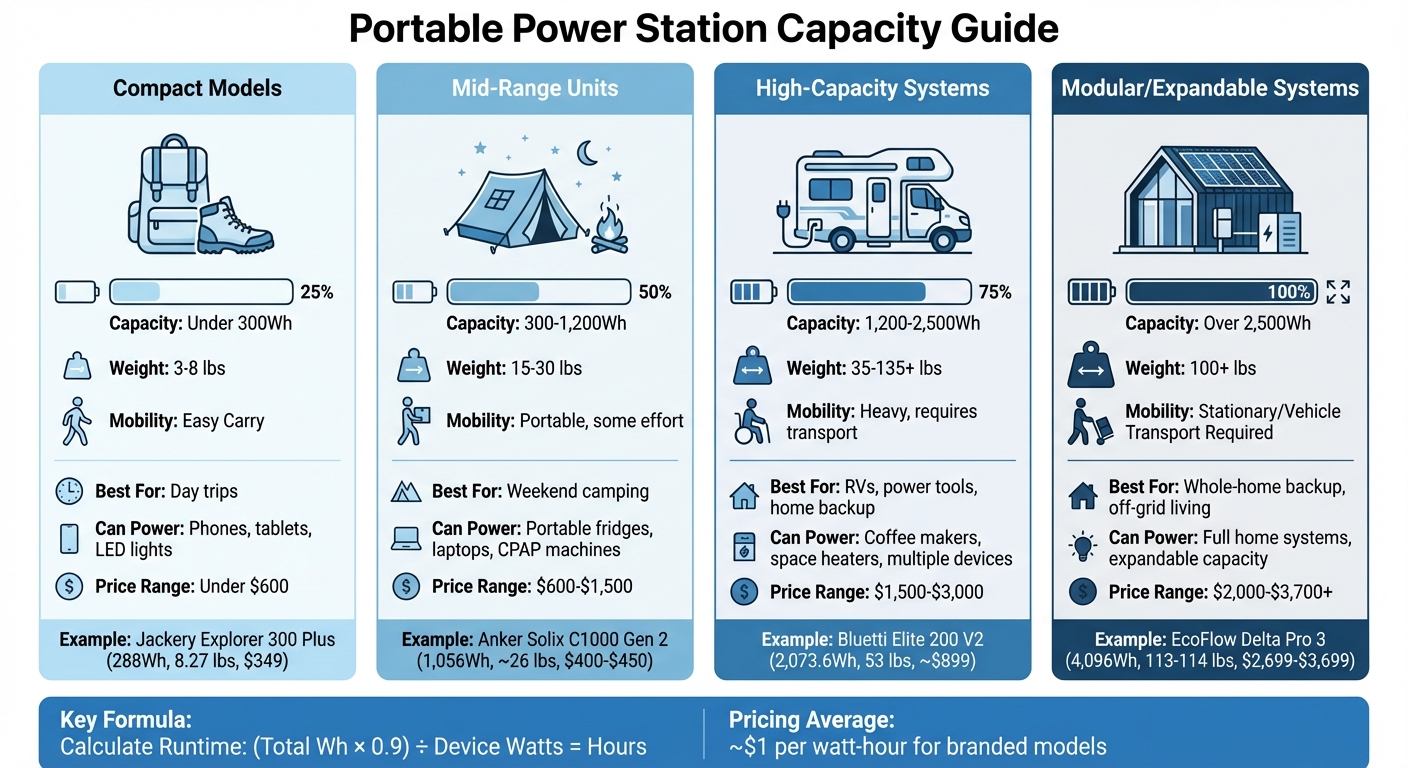
Portable Power Station Capacity Guide: Choosing the Right Size for Your Outdoor Activities
Main Features of Portable Power Stations
Knowing the key components of a portable power station can help you pick the right one. One of the most important factors is battery capacity, measured in watt-hours (Wh). This tells you how much energy the station can store. For example, a 1,000Wh unit theoretically powers a 100W device for 10 hours. However, real-world efficiency - typically around 80–90% - means you’ll get closer to 850Wh of usable energy due to inverter losses.
Power output is another critical feature, broken into two categories: continuous watts (steady power for ongoing use) and surge watts (short bursts needed to start devices like refrigerators or power tools). If you’re running something like a portable fridge, check that the station’s surge rating can handle the initial power spike. The inverter type also plays a role. Pure sine wave inverters are ideal for sensitive electronics like laptops or medical devices, as they replicate the quality of grid power. In contrast, modified sine wave inverters can cause issues like overheating or noise.
When it comes to battery chemistry, most modern stations use LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) batteries. These are more durable, perform better in extreme temperatures, and last longer compared to standard lithium-ion batteries. Output options include AC outlets (for household devices), USB-A, USB-C Power Delivery (great for laptops), and 12V DC car ports. Charging options are versatile as well - most stations support AC wall charging, 12V car charging, and solar panels. Some models now even offer fast-charging capabilities, going from 0% to 80% in under an hour.
With these features in mind, portable power stations can be grouped by their capacity and use cases.
Types by Capacity and Use
Portable power stations come in different sizes, each suited to specific needs.
- Compact models (under 300Wh): These lightweight units, weighing between 3–8 lbs, are perfect for day trips. They can charge phones, tablets, and LED lights.
- Mid-range units (300–1,200Wh): Weighing 15–30 lbs, these are ideal for weekend camping trips. They can power portable fridges, laptops, and CPAP machines.
- High-capacity systems (1,200–2,500Wh): Designed for RVs, power tools, or home backup, these units weigh 35–135+ lbs and require vehicle transport.
- Modular or expandable systems (over 2,500Wh): These are scalable solutions for whole-home backup or off-grid living.
Mobility is a key factor when choosing the right station. Compact models fit easily in a backpack for hiking, while mid-range units strike a balance between portability and power for extended camping. High-capacity systems are less portable but provide the energy needed for larger setups like RVs or basecamps.
Pricing generally aligns with capacity, averaging about $1 per watt-hour for branded models. Entry-level units under 500Wh often cost less than $600. Mid-range models (500–1,500Wh) range from $600 to $1,500, while high-capacity systems (over 1,500Wh) can cost $1,500 to $3,000 or more. To ensure you have enough power, calculate your needs and add a 25% buffer for conversion losses and surges. For smaller electronics, prioritize using 12V DC or USB ports instead of AC outlets to avoid unnecessary energy loss from the internal inverter.
What to Consider for Outdoor Use
Battery Capacity and Power Output
Choosing the right power station for your outdoor adventures can make or break your experience. For hiking and backpacking, lightweight units between 150Wh and 500Wh are ideal. These weigh just 3–15 lbs and are perfect for keeping essentials like phones, GPS devices, and headlamps charged without adding too much bulk. If you're into weekend car camping, consider mid-range stations with capacities from 500Wh to 1,200Wh. These can handle portable fridges, LED lights, and even laptops for a few days. For longer trips or RV excursions, you'll need something more robust - high-capacity units (1,200Wh to 2,500Wh+) can power coffee makers, CPAP machines, or even space heaters for multiple nights.
Capacity alone isn’t enough, though. Power output is just as important. A station’s continuous AC output must be higher than the wattage of your most power-hungry device. At the same time, surge power handles those brief but intense energy spikes when devices with motors, like refrigerators, start up.
To estimate how long your power station will last, use this formula: (Total Watt-hours × 0.9) ÷ Device Watts = Hours of runtime. Keep in mind, real-world capacity usually falls between 70% and 93% due to energy losses during conversion. Cold weather also affects performance - lithium batteries can lose up to 25% of their capacity in temperatures between 0°F and 20°F, and even more when it drops below zero.
Now, let’s dive into how portability and durability factor into your decision.
Portability and Durability
If you’re carrying your power station to remote spots, weight is a big deal. Units in the 1,000Wh range typically weigh 20–30 lbs, making them manageable for mobile activities like hiking. For base camps or RV setups, heavier units are fine since you’re prioritizing capacity over portability.
"Portability is one of the most important factors when choosing a power station for camping. Size and weight are significant considerations if you routinely pull out your power station at a campsite." - Alan Rogers Guide
Design features can make a surprising difference. Fold-down handles are great for saving space in your car or on a shelf, while fixed handles can make packing awkward. For rugged environments, check for units with IP ratings - an IP67 rating means waterproofing, while IPX4 offers splash resistance from any angle. A tough outer shell is also key to preventing damage during transport, especially on bumpy trails.
The type of battery also plays a role in weight and durability. LiFePO4 batteries are bulkier but built to handle rugged conditions and last longer. On the other hand, lithium-ion (NMC) batteries are lighter and better suited for backpacking.
Solar Compatibility and Charging Options
For trips lasting more than three days without access to AC power, solar charging is a game-changer. It allows you to recharge your station daily instead of rationing power. A good rule of thumb: you’ll need 200W of solar panel capacity for every 1,000Wh of battery capacity. For example, a 200W panel will take about 6.3 hours of peak sunlight to fully charge a 1,000Wh station. Solar charging efficiency typically ranges from 75% to 85%.
Stations equipped with MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) controllers are your best bet. They’re more efficient at managing solar input compared to PWM controllers and help extend battery life. Some advanced models even support dual charging (AC + solar simultaneously), which significantly reduces recharge times.
Don’t forget other charging options. AC wall charging is the fastest - some units can go from 0% to 80% in under an hour, making it perfect for pre-trip prep or campsites with power hookups. 12V car adapters are slower but handy for topping off while driving. Smaller units with USB-C Power Delivery can charge at speeds up to 100W, offering a middle ground. For better efficiency when outdoors, use 12V DC outputs for devices like portable fridges instead of AC outlets - this avoids inverter losses and extends runtime.
Recommended Portable Power Stations for Outdoor Adventures
Choosing the right portable power station means balancing capacity, features, and portability to suit your specific outdoor needs. Currently, 1,000Wh models are priced between $380 and $450, making them an appealing option for outdoor enthusiasts. Key factors like output power and weight often tip the scales when deciding which model to pick. Below are some top recommendations, each catering to different types of adventures.
The Anker Solix C1000 Gen 2 is a great all-around choice for weekend camping trips or general outdoor use. It boasts a continuous output of 2,000W and recharges fully in just 49 minutes - a standout feature in its class. OutdoorGearLab awarded it a score of 66/100, calling it "Best for Most People" for its balance of power and price. At around $400–$450, it’s a versatile option for various activities.
For backpackers or those seeking an ultralight unit, the Jackery Explorer 300 Plus is a strong contender. Weighing just 8.27 lbs, it delivers 288Wh and includes an AC outlet, unlike many similar-sized models that only feature USB outputs. Priced at approximately $349, it’s a convenient choice for lightweight power needs. If you need more capacity but still value portability, the Jackery Explorer 1000 v2 offers 1,000Wh in a lightweight 23.8-lb package, making it the lightest in its category.
For larger setups like RVs or off-grid cabins, the EcoFlow Delta Pro 3 is a powerhouse. It provides 4,096Wh with a continuous output of 4,000W (expandable to 6,000W using X-Boost) and can scale up to 48kWh with additional batteries. Rated "Best for Home Backup" with a score of 81/100, it’s ideal for stationary use. However, its hefty weight of 113–114 lbs and price tag of $2,699 ($3,699 MSRP) make it a better fit for those who need serious capacity. For a more mid-range option, the Bluetti Elite 200 V2 delivers 92% of its rated 2,073.6Wh capacity, earning it the title of "Best Overall" from Popular Mechanics. Priced at about $899, it's a solid pick for extended trips.
Model Comparison Table
| Model | Capacity | Power Output (Continuous / Peak) | Weight | Price Range (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anker Solix C1000 Gen 2 | 1,056 Wh | 2,000 W / 2,400 W | ~26 lbs | $400 – $450 |
| Jackery Explorer 300 Plus | 288 Wh | 300 W / 600 W | 8.27 lbs | ~$349 |
| Jackery Explorer 1000 v2 | 1,070 Wh | 1,500 W / 3,000 W | 23.8 lbs | $380 – $450 |
| Bluetti Elite 200 V2 | 2,073.6 Wh | 2,600 W / 3,900 W | 53 lbs | ~$899 |
| EcoFlow Delta Pro 3 | 4,096 Wh | 4,000 W / 6,000 W* | 113–114 lbs | $2,699 – $3,699 |
*With X-Boost technology.
Most modern power stations now use LiFePO4 batteries, known for their long-lasting performance. Keep in mind, though, that real-world usage typically delivers about 85% of the listed watt-hours due to energy conversion losses. Additionally, extreme cold - around –20°F - can reduce capacity by 35–45%. To mitigate this, store your power station in an insulated bag or inside your vehicle to maintain over 90% of its rated capacity.
Usage and Maintenance Tips
Safe Usage Outdoors
Most portable power stations aren't designed to handle water exposure, so it's crucial to keep them away from rain, snow, or any standing water. They function best within a temperature range of 14°F to 104°F (-10°C to 40°C). High heat can be especially dangerous - avoid leaving them in hot cars or under direct sunlight, as this can lead to overheating, fire, or even explosions.
Make sure the ventilation areas remain unobstructed to prevent overheating. After outdoor use, wipe these areas with a dry cloth to remove any accumulated dust or debris. Never exceed the "continuous watts" rating of your power station. While surge watts are meant to handle short bursts of power, going beyond the continuous limit will activate overload protection and shut the unit down. If you're using high-power devices with long extension cords, ensure the cords are fully uncoiled to avoid overheating.
For energy efficiency, manually turn off both AC and DC outputs when the power station is idle to prevent unnecessary battery drain. Some models allow pass-through charging (using the station while it's recharging), but using this feature too often can generate excess heat and shorten the battery's lifespan. Use it sparingly to avoid wear and tear.
While safe outdoor operation is key, taking care of the battery is just as important to ensure long-term performance.
Battery Care and Maintenance
Proper battery care is essential for extending your power station's lifespan. Recharge the battery once it drops below 20% capacity, and avoid letting it hit 0%, as deep discharges can damage the battery permanently. For long-term storage (over three months), aim to keep the battery at 50% to 60% charge and recharge it every three months to prevent over-discharge. Fully charging the battery for storage can lead to a 20% capacity loss per year, but storing it at 40% charge reduces this to just 4%.
"Lithium batteries will most often degrade due to three main reasons: time, charge cycles, and environment." - Anker
Store your unit in a cool, dry location with temperatures between 50°F and 77°F (10°C to 25°C). Even when not in use, lithium batteries naturally lose about 3% of their capacity each month. To maintain performance, perform a "mini-cycle" every three to six months: use the power station to run a small load, then recharge it to the recommended 50–60% storage level. Keep vents and ports clean by using compressed air or a dry toothbrush. Additionally, check for firmware updates regularly, as they can improve energy efficiency and address any issues affecting battery stability.
Conclusion
Choosing the right portable power station means aligning its capacity and output with your specific outdoor needs. To avoid overloads, ensure the station’s wattage exceeds your combined device requirements by 10–25%. Also, keep in mind that the actual capacity is often about 80% of the advertised rating. This careful planning ensures reliable performance, but long-term functionality depends heavily on battery type and proper care.
When it comes to battery chemistry, LiFePO4 batteries stand out for their durability. They can last 10–15 years, compared to the 3–5 years typical of standard lithium-ion batteries. Although slightly heavier, their extended lifespan and safety features make them a great choice for frequent outdoor use.
Maintenance is just as important as selection. To protect your investment, store the power station at 50–60% charge in a temperature range of 50°F to 77°F (10°C to 25°C). Perform mini-cycles every three to six months, and avoid discharging the battery below 20%.
"A portable power station is a valuable tool for anyone who needs a reliable source of electricity on the go. Whether you're camping in the wilderness... a portable power station can provide the power you need, whenever and wherever you need it." - Renewable Outdoors
Portable power stations bring quiet, clean energy to outdoor adventures, powering everything from medical devices to portable fridges - without the noise and fumes of traditional gas generators. Pairing one with solar panels creates a self-sustaining, zero-emission power source, ensuring you stay connected and comfortable no matter where your journey takes you. By following the tips in this guide, you’ll be well-equipped to make the most of your outdoor experiences.
FAQs
How do I size a power station for my gear?
To choose the right power station, start by figuring out the total wattage of all the devices you plan to power. You can usually find each device's wattage on its label or in its manual. Once you have the wattage for all devices, add them together.
Next, calculate the energy capacity you'll need in watt-hours (Wh). Do this by dividing the total wattage by the expected runtime. For example, if your devices collectively use 500 watts and you need them to run for 2 hours, you'll need a power station with at least 1,000 Wh of capacity.
Finally, check if the power station can handle peak wattage. Some devices, like refrigerators or power tools, require extra wattage when they start up. Make sure the power station can support these startup surges to avoid issues.
By following these steps, you can confidently pick a power station that matches your energy needs.
Will it run a fridge, CPAP, or power tools safely?
A portable power station can keep essential devices like refrigerators, CPAP machines, and power tools running - if its capacity and output match the power demands of those devices. For instance, a station with a 1,500Wh capacity and 1,800W output could power a refrigerator for 8 to 12 hours or a CPAP machine for 2 to 3 nights. To use it safely, always compare the station's wattage and surge capacity with the requirements of your devices.
What solar panel wattage do I need to recharge it?
When deciding on the right solar panel wattage for your portable power station, consider the station's capacity and how fast you need it to charge. A good rule of thumb is to select a panel with wattage equal to or greater than the station's input capacity. For instance, pairing a 200W solar panel with a 200Wh power station ensures efficient and reliable charging.
