
How AI Optimizes Power Generation Systems
Share
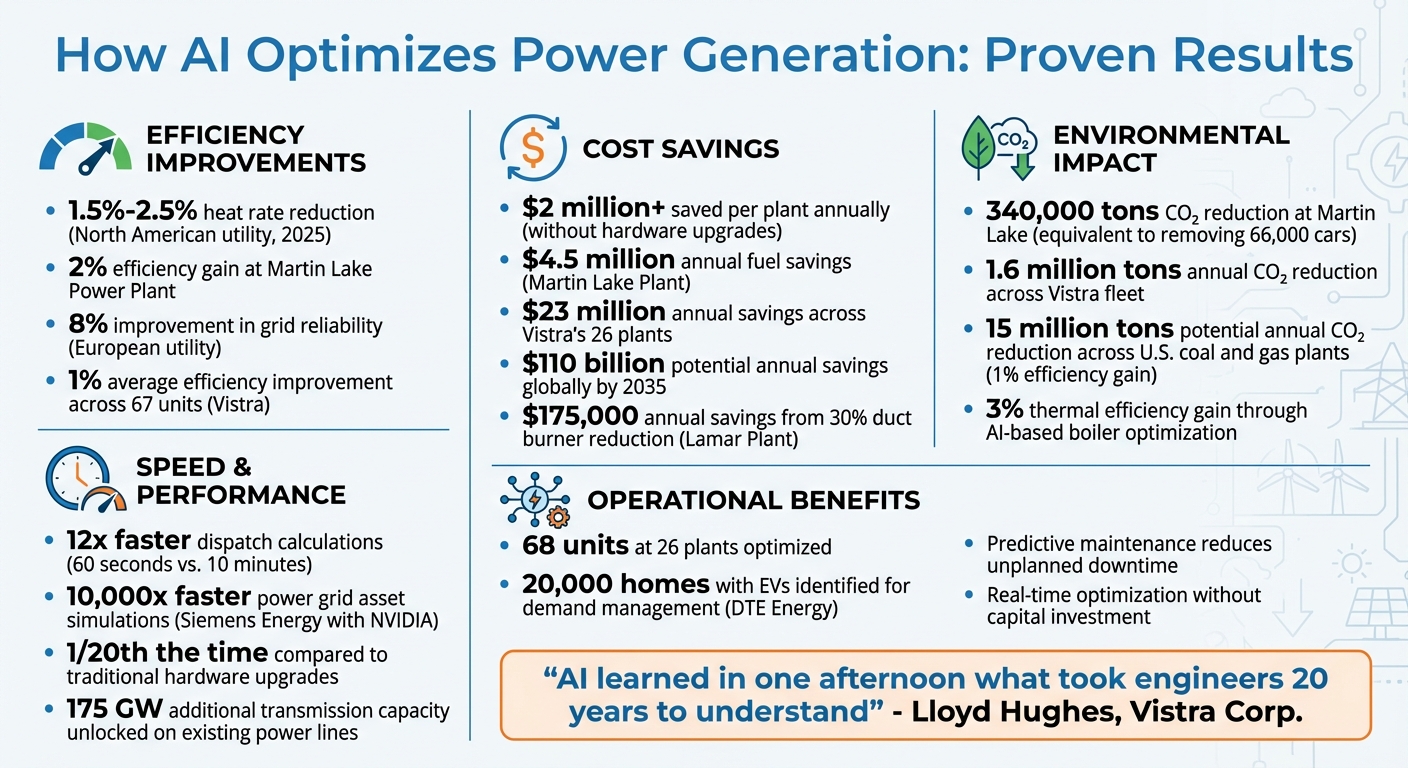
AI is transforming power generation by making systems more efficient, cost-effective, and reliable. Through real-time data analysis, machine learning models, and predictive maintenance, AI helps power plants save millions annually while reducing fuel consumption and emissions. For example, in 2025, a North American utility used AI to cut heat rates by 1.5%-2.5%, saving over $2 million per plant without hardware upgrades. AI also improves grid stability by forecasting demand and managing renewable energy fluctuations.
Key takeaways:
- AI reduces fuel consumption and improves efficiency.
- Predictive maintenance minimizes unplanned outages.
- AI balances renewable energy integration with grid stability.
- Savings potential: Up to $110 billion annually by 2035.
The combination of AI-powered tools and reliable hardware is reshaping the energy sector, offering both financial and environmental benefits.
AI Power Generation Optimization: Key Benefits and Cost Savings
How AI Analyzes Data to Optimize Power Generation
Data Collection and Sensor Integration
Modern power plants rely heavily on data to achieve AI-driven optimization. At the heart of this process is the Distributed Control System (DCS), which collects high-frequency sensor data. This data includes a wide range of metrics like ambient temperature, load levels, steam pressures, valve positions, and fuel flow rates. For Combined Cycle Gas Turbines (CCGT), key data points include inlet guide vane positions, ambient humidity, and condenser backpressure. In contrast, coal-fired plants focus on metrics such as pulverizer performance, excess air ratios in boilers, and flue gas oxygen content.
The quality of the data plays a critical role in AI performance. As John Karigiannis, AI & Robotics Technology Manager at GE Vernova, explains:
"AI models rely on vast, high-quality datasets that represent asset operations. Sufficient and clean data is essential so that when a model learns a particular process or how an asset operates, it has the ability to see a snapshot of the operation".
To ensure accurate model training, operators must calibrate sensors and verify data integrity. Once high-quality data is secured, AI models can deliver precise predictions for optimizing performance.
Machine Learning Models for Predictive Analysis
After the data is collected, neural networks step in to analyze it. These models process historical data to learn thermodynamic relationships, with the ultimate goal of predicting "optimal" performance under current conditions. By comparing these predictions to real-time performance, inefficiencies caused by control settings or equipment wear become evident. This insight allows for adjustments that enhance efficiency.
Advanced tools like SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) provide engineers with clarity on which variables are impacting efficiency. For instance, SHAP can highlight how factors like inlet guide vane position or excess air ratio influence performance. This level of transparency ensures that the model is identifying genuine thermodynamic principles rather than irrelevant patterns.
The speed at which these models learn is remarkable. Lloyd Hughes, a Technical Expert at Vistra Corp, noted:
"There are things that took me 20 years to learn about these power plants. This model learned them in an afternoon".
In 2024, Vistra implemented a Heat Rate Optimizer across 68 units at 26 plants, using Bayesian regression and deep-learning models. At the Lamar Power Plant in Texas, Operations Manager Patrick "Cade" Hay reported a 30% reduction in duct burner usage, leading to fuel cost savings of approximately $175,000 annually and a smaller carbon footprint.
Beyond boosting efficiency, these models also support predictive maintenance. By analyzing sensor data, AI can detect anomalies in components like turbine blades, boiler tubes, and condensers before they fail. This allows plants to move from rigid maintenance schedules to condition-based strategies, reducing unplanned downtime and extending the lifespan of critical equipment - an essential shift for facilities operating under tight financial constraints.
sbb-itb-501186b
Enhancing Energy Systems: Using AI for Power Plant Energy Management
Building Operational Constraints into AI Systems
As AI reshapes power generation, incorporating physical limits and expert oversight is essential to ensure predictions translate into safe, practical improvements.
Defining Operational Boundaries
AI predictions must respect the physical limits of real-world equipment. Power plants operate within tightly controlled parameters - steam pressure thresholds, combustion temperature ranges, turbine speed limits, and grid stability requirements. If these constraints aren’t built into AI systems, recommendations could push equipment beyond safe operating conditions, leading to failures or even regulatory non-compliance.
To address this, technologies like digital twins simulate equipment behavior, allowing operators to test optimization strategies without real-world risks. These simulations ensure AI recommendations stay within safe equipment limits, such as managing cooling demands when power densities exceed 100 kW. Similarly, grid-to-token efficiency modeling treats the entire energy ecosystem - generation, distribution, and consumption - as an integrated system, ensuring both electrical and thermal constraints are respected.
Thermal management is also becoming a pressing challenge as hardware demands grow. While traditional data center racks typically consume 5–10 kW, AI-specific racks now surpass 100 kW, with projections reaching up to 650 kW in the future. To prevent overheating and performance issues, AI systems must factor in advanced cooling techniques, such as Direct-to-Chip (DLC) or immersion cooling. Ben Lorica, Editor at Gradient Flow, highlights the importance of this approach:
"An optimized facility offers more compute per dollar and watt".
These operational boundaries lay the groundwork for expert review, ensuring AI outputs are not only efficient but also safe and compliant.
Validation with Domain Expertise
Once operational limits are defined, domain experts play a critical role in validating AI recommendations. Even the most advanced AI models require human oversight to ensure their outputs align with real-world conditions and regulatory standards. Domain experts validate AI outputs by cross-checking them against practical experience, safety protocols, and constraints that may not be fully captured in the training data. This human-in-the-loop approach bridges the gap between algorithmic predictions and operational feasibility.
John Karigiannis, AI & Robotics Technology Manager at GE Vernova, underscores the importance of this collaboration:
"Even the most advanced AI models often require human interaction to deliver accurate outcomes".
Effective validation depends on transparent AI interfaces that help operators understand why specific recommendations are made. Providing plant personnel with clean, high-quality data and educational resources builds trust and ensures smoother integration of AI systems.
For instance, in 2024, Siemens Energy leveraged the NVIDIA Modulus framework to speed up power grid asset simulations by an astonishing 10,000 times. By creating detailed digital twins capable of simulating stress scenarios, they improved predictive maintenance while ensuring AI recommendations adhered to strict operational boundaries. Similarly, Southern California Edison (SCE) collaborated with NVIDIA to enhance incident management during major power disruptions, using domain-specific data to ensure safety and compliance.
AI in Grid Management and Renewable Integration
AI's contributions to energy systems continue to expand, particularly in grid management and the integration of renewable energy sources. Beyond defining and validating operational limits, AI now plays a critical role in balancing the variability of renewables like wind and solar with grid stability. Since renewable energy sources fluctuate unpredictably, maintaining a constant balance between supply and demand is one of the energy sector's most pressing challenges. AI steps in to make this balancing act not only possible but efficient, even as the complexity of the grid increases.
Demand Forecasting and Waste Reduction
AI reshapes demand forecasting by analyzing a mix of historical and real-time data, such as weather patterns, consumer habits, and seasonal trends, to predict energy needs with impressive precision. Unlike older deterministic models that offer single-point predictions, machine learning models generate probabilistic forecasts, preparing utilities for a range of scenarios and reducing uncertainty.
In a notable example from 2019, scientist Feng Qiu from Argonne National Laboratory collaborated with the Midcontinent Independent System Operator (MISO) to test an AI-powered model for daily grid planning. This system completed dispatch calculations 12 times faster than traditional methods, cutting the process from nearly 10 minutes to just 60 seconds. This speed allows utilities to make real-time adjustments, minimizing energy waste and lowering operational costs.
AI also introduces "demand flexibility", identifying opportunities to shift energy-intensive tasks to off-peak hours. For instance, Detroit-based utility DTE Energy partnered with the startup WeaveGrid to pinpoint 20,000 homes with electric vehicles (EVs) in its service area. Using this data, the utility developed precise long-term load forecasts to handle the increased demand caused by EV clustering in specific neighborhoods. By coordinating EV charging schedules, utilities can shift energy consumption to times when renewable energy is more abundant or when overall demand is lower. These advancements in forecasting create a dynamic system capable of adapting to the fluctuations of renewable energy sources.
Grid Balancing and Renewable Energy Integration
Accurate forecasts are just the beginning. AI also ensures grid stability by managing distributed energy resources, a task made more complex by renewables' inherent variability. Solar panels, for instance, generate no power at night, and wind turbines become inactive without wind. AI mitigates these challenges by coordinating a network of distributed resources - electric vehicles, home batteries, and smart thermostats - to stabilize the grid in real time.
One example is Lunar Energy’s "Gridshare" AI software, which collects data from tens of thousands of homes. By combining information on individual appliance usage with weather forecasts, the system predicts energy needs for each household. This aggregated data allows homes to act as responsive grid assets. When renewable energy supply surges or demand dips, AI can adjust energy consumption across thousands of devices almost instantly.
Anuradha Annaswamy, a Senior Research Scientist at MIT, highlights the need for a robust information infrastructure to complement the physical grid:
"Essentially you need to introduce a whole information infrastructure to supplement and complement the physical infrastructure".
This additional layer of information enables AI to dynamically balance supply and demand. The potential economic benefits are enormous: AI applications in power plant operations and maintenance could save up to $110 billion annually by 2035, while unlocking up to 175 GW of extra transmission capacity on existing power lines. By making renewable energy integration both feasible and cost-effective, AI ensures that grid reliability is maintained even as the energy landscape evolves. These advancements echo the broader use of AI across power plant systems, enhancing resilience at both individual and systemic levels.
Measured Benefits of AI in Power Generation
AI is reshaping power generation by delivering tangible cost savings and boosting efficiency. Real-world applications have shown how AI can achieve millions in annual savings without requiring new capital investments. These results are largely driven by heat rate optimization, which minimizes the fuel needed to produce electricity, and predictive maintenance, which helps avoid expensive, unexpected outages. Together, these advancements bring financial and environmental benefits that are hard to ignore.
Performance Improvements and Cost Savings
In October 2020, Vistra Corp. implemented an AI-powered Heat Rate Optimizer at its Martin Lake Power Plant in Tatum, Texas. The results were impressive: a 2% efficiency gain, $4.5 million in annual fuel savings, and a reduction in carbon emissions by 340,000 tons - equivalent to taking 66,000 cars off the road. Lloyd Hughes, Operations Manager at Vistra Corp., praised the technology, saying:
"There are things that took me 20 years to learn about these power plants. This model learned them in an afternoon".
Encouraged by the success, Vistra expanded the solution to 67 power-generation units across 26 plants, achieving an average 1% improvement in efficiency. This fleet-wide deployment resulted in over $23 million in annual savings and cut carbon emissions by 1.6 million tons each year.
Another example comes from a leading North American utility that used AI for heat rate optimization across multiple coal and combined cycle gas turbine (CCGT) units. The initiative delivered a 1.5% to 2.5% reduction in heat rate, with one coal plant alone saving over $2 million annually - all without requiring any equipment upgrades. In Europe, a utility applied AI for dynamic load forecasting and achieved an 8% improvement in grid reliability, reducing costs tied to outages and balancing.
The global potential of AI in power generation is enormous. By 2035, AI could save up to $110 billion annually in operational and maintenance costs worldwide while unlocking 175 GW of additional transmission capacity in existing power lines. And it’s fast - AI-driven heat rate optimization can deliver results in 1/20th of the time it takes for traditional hardware upgrades.
Environmental Impact and Emissions Reduction
The environmental benefits of AI in power generation are equally compelling. Even a modest 1% efficiency improvement across U.S. coal and gas plants could slash carbon emissions by 15 million tons annually, which is comparable to shutting down two large coal plants or planting 37 million trees. AI-based boiler optimization has shown even greater potential, with studies documenting a 3% gain in thermal efficiency, significantly cutting both fuel use and greenhouse gas emissions.
AI isn't just optimizing existing systems - it’s paving the way for cleaner energy technologies. By accelerating the discovery of advanced materials, AI reduces development timelines for innovations like new battery chemistries, perovskites for solar cells, and materials for nuclear reactors. As Ju Li, a Professor of Power Engineering at MIT, explains:
"AI has the potential to lubricate the material-discovery and optimization process, perhaps shortening it from decades as in the past to just a few years".
This dual role - enhancing current fossil fuel systems while speeding up the transition to renewable energy - positions AI as a critical tool in addressing both today’s energy challenges and tomorrow’s sustainability goals.
Deploying AI Solutions Across Power Plant Fleets
Rolling out AI across power plants isn't a one-size-fits-all process. Each plant has its own unique characteristics - whether it's the age of the equipment, local climate conditions, or its operational history. The trick lies in finding the right mix of standardization and customization, so solutions that work well in one plant can be tailored and applied across the entire fleet without losing their effectiveness.
Baseline Analysis and Model Training
The first step? Establishing a clear baseline for each plant. This involves gathering high-frequency historical DCS (Distributed Control System) data to define how the plant typically operates. The data should cover a wide range of variables, including ambient temperature, humidity, steam pressures, fuel flow rates, and even pulverizer performance. By analyzing this historical data, you can uncover how the plant performs under different conditions and pinpoint areas where efficiency can be improved.
The AI model is then trained to focus on metrics specific to each plant’s operations. For instance, a combined cycle gas turbine (CCGT) model will prioritize parameters like gas turbine load and inlet guide vane positions. Meanwhile, a coal-fired plant model zeroes in on metrics like flue gas oxygen levels and excess air ratios to optimize combustion efficiency. As John Karigiannis, AI & Robotics Technology Manager at GE Vernova, explains:
"Clean, comprehensive data enables the model to accurately capture each asset's operational snapshot".
Once the model is trained, it undergoes rigorous testing and validation. Plant engineers use tools like SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) to ensure that the AI’s recommendations align with both thermodynamic principles and practical engineering knowledge. After passing these validation checks, the insights are ready to be integrated into the plant’s control systems.
Integration with Control Systems
After building reliable models, the next challenge is embedding them into the plant’s existing control infrastructure. This involves creating user-friendly interfaces in the control room that deliver real-time optimization recommendations, complete with clear, contextual explanations.
Safety is a top priority during this process. The system includes strict operational safeguards, such as limiting temperature increases to no more than 5°F over a 15-minute period. It also pauses recommendations during load changes until the plant stabilizes. Barry Boswell, Executive Vice President of Power-Generation Operations at Vistra Corp., shared an important lesson learned during their deployment:
"If our plant managers aren't bought in, then things don't happen. So, we said, 'Let's pick a leader who is knowledgeable and skeptical, because if we can win them over, we can get everyone'".
IT teams play a crucial role here, ensuring smooth integration by configuring virus scanner exclusions for AI-related folders to avoid disruptions. As Anuradha Annaswamy, Senior Research Scientist at MIT, points out:
"Essentially you need to introduce a whole information infrastructure to supplement and complement the physical infrastructure".
This integration process not only ensures each plant operates safely and efficiently but also enhances the overall performance of the entire power plant fleet.
Conclusion
AI is reshaping the way power generation systems operate, achieving efficiency improvements and cost savings that once seemed years away. By leveraging advanced machine learning models, plants can analyze intricate thermodynamic processes to uncover optimization opportunities - without needing costly hardware upgrades.
The benefits go beyond just financial gains. These systems are helping the industry move toward cleaner energy by enhancing renewable energy integration and cutting emissions. It’s a win-win: operational efficiency paired with a commitment to reducing environmental impact.
But here’s the catch - none of this works without a solid physical foundation. Accurate sensors, well-calibrated equipment, and reliable electrical components are essential for feeding high-quality data into AI models. Without these, even the smartest algorithms won’t deliver meaningful results.
For facilities aiming to adopt AI-driven optimization, investing in dependable hardware is the first step. Platforms like Electrical Trader offer a range of essential components - transformers, breakers, sensors, and power distribution equipment - that are critical for creating the infrastructure AI systems need. Whether you’re upgrading a single plant or rolling out solutions fleet-wide, access to both new and reconditioned equipment can make the process more affordable. With the right tools in place, any plant can unlock AI’s potential.
The combination of advanced AI software and high-quality physical components is redefining modern power generation. The tools are available, the results are proven - the only question is how quickly your operation can take advantage of this transformation.
FAQs
How does AI enhance power generation efficiency without requiring new hardware?
AI is transforming power generation by analyzing real-time data to fine-tune operations and boost efficiency. By using machine learning to process information like sensor readings, fuel consumption, and equipment performance, AI can optimize settings for critical components such as valves and turbines. This means power plants can achieve higher output without needing expensive physical upgrades. These adjustments can lower heat rates by 1.5%–2.5%, translating to millions in fuel savings and reduced emissions.
AI also plays a key role in energy management. It predicts demand, balances renewable energy inputs, and spots equipment issues before they lead to downtime. For example, AI systems have cut fuel usage by as much as 30% in some cases, delivering substantial cost savings while extending the lifespan of equipment. By combining AI-driven insights with top-tier components - like those offered by Electrical Trader - plant managers can get the most out of their current systems and avoid the expense of major retrofits.
How does AI help integrate renewable energy into the power grid?
AI is transforming how renewable energy integrates into power grids, especially when it comes to managing the unpredictable nature of solar and wind energy. By leveraging advanced machine learning, AI processes real-time data from sources like weather forecasts, sensors, and satellites to predict energy production with impressive accuracy. With these insights, grid operators can better balance supply and demand, scheduling resources like conventional power plants, energy storage, and demand-response systems more effectively.
Beyond forecasting, AI enhances grid performance by fine-tuning elements like voltage, frequency, and line loads in real time. This creates a self-adjusting grid that minimizes wasted renewable energy, boosts efficiency, and supports the transition to a cleaner energy system. However, achieving these outcomes depends on reliable hardware - smart meters, advanced inverters, and communication modules all play a key role. Platforms such as Electrical Trader provide a variety of electrical components and tools essential for modernizing grids with AI technology.
How does AI-powered predictive maintenance help avoid unexpected power plant outages?
AI-driven predictive maintenance uses sensor data from equipment like turbines, boilers, and generators to spot early signs of wear or unusual behavior. By leveraging machine learning, these systems compare current data with historical performance, picking up on subtle changes that might slip past human observation. This enables operators to tackle potential problems before they escalate into expensive breakdowns.
With the ability to forecast failures days - or even weeks - in advance, AI allows for repairs to be scheduled during planned downtimes or sometimes even while the equipment is running. This forward-thinking strategy can cut maintenance costs by up to 30% and boost equipment availability by about 20%. Plus, platforms such as Electrical Trader can supply the required parts quickly, ensuring repairs are done promptly and reducing the chances of unexpected outages.
