Cable Fault Testing Tools Compared
Share
Finding the right cable fault testing tool can save you time, money, and frustration. Here's a quick breakdown of the top tools and their key features:
- Klein Tools Scout Pro Max Network Cable Tester: Ideal for network troubleshooting, supports RJ11, RJ12, RJ45, and F-connector cables. Priced at $479.99, it uses TDR technology for precise fault detection up to 2,000 feet.
- Fluke Networks TS 90 Cable Fault Finder: Simplifies fault location with clear distance readings. Works on cables up to 2,500 feet and costs around $300-$400.
- HD Electric UCT-8/K01 Underground Cable Fault Tester: Designed for underground cables, handles lengths up to 1,500 feet. Priced at $2,047.87, it’s perfect for utility companies.
- Fluke Networks MicroMapper: Compact and affordable ($173-$175), it’s great for Ethernet cable testing and detecting faults like split pairs.
- Fluke Networks IntelliTone Pro 200: Combines digital and analog signals for versatile cable tracing. Costs $335.60+ and works well with both data and voice cables.
Quick Comparison Table
| Tool Name | Price Range | Max Cable Length | Key Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Klein Tools Scout Pro Max | $479.99 - $499.99 | 2,000 feet | TDR technology, PoE testing, shielded/unshielded | Network troubleshooting |
| Fluke Networks TS 90 | $300 - $400 | 2,500 feet | Simple distance readings, SmartTone tech | Fieldwork fault location |
| HD Electric UCT-8/K01 | $2,047.87 | 1,500 feet | DC leakage testing, underground cable focus | Utility companies, contractors |
| Fluke Networks MicroMapper | $173 - $175 | 656 feet | LED wiremap, split pair detection | Ethernet cable testing |
| Fluke Networks IntelliTone Pro 200 | $335.60+ | Varies | Digital/analog tracing, NIC/hub indication | Active/live network tracing |
Key Takeaway
Choose a tool based on your specific needs:
- For network troubleshooting, go with the Klein Tools Scout Pro Max or Fluke Networks IntelliTone Pro 200.
- If you work with underground cables, the HD Electric UCT-8/K01 is your best option.
- For basic Ethernet cable testing, the Fluke Networks MicroMapper offers affordability and simplicity.
- Need a field-friendly fault finder? The Fluke Networks TS 90 is a solid choice.
Start with your budget and testing requirements to find the tool that fits your work best.
TOP 5 NETWORK CABLE TESTERS FOR 2024 - ULTIMATE BUYER'S GUIDE
1. Scout Pro Max Network Cable Tester (Klein Tools)
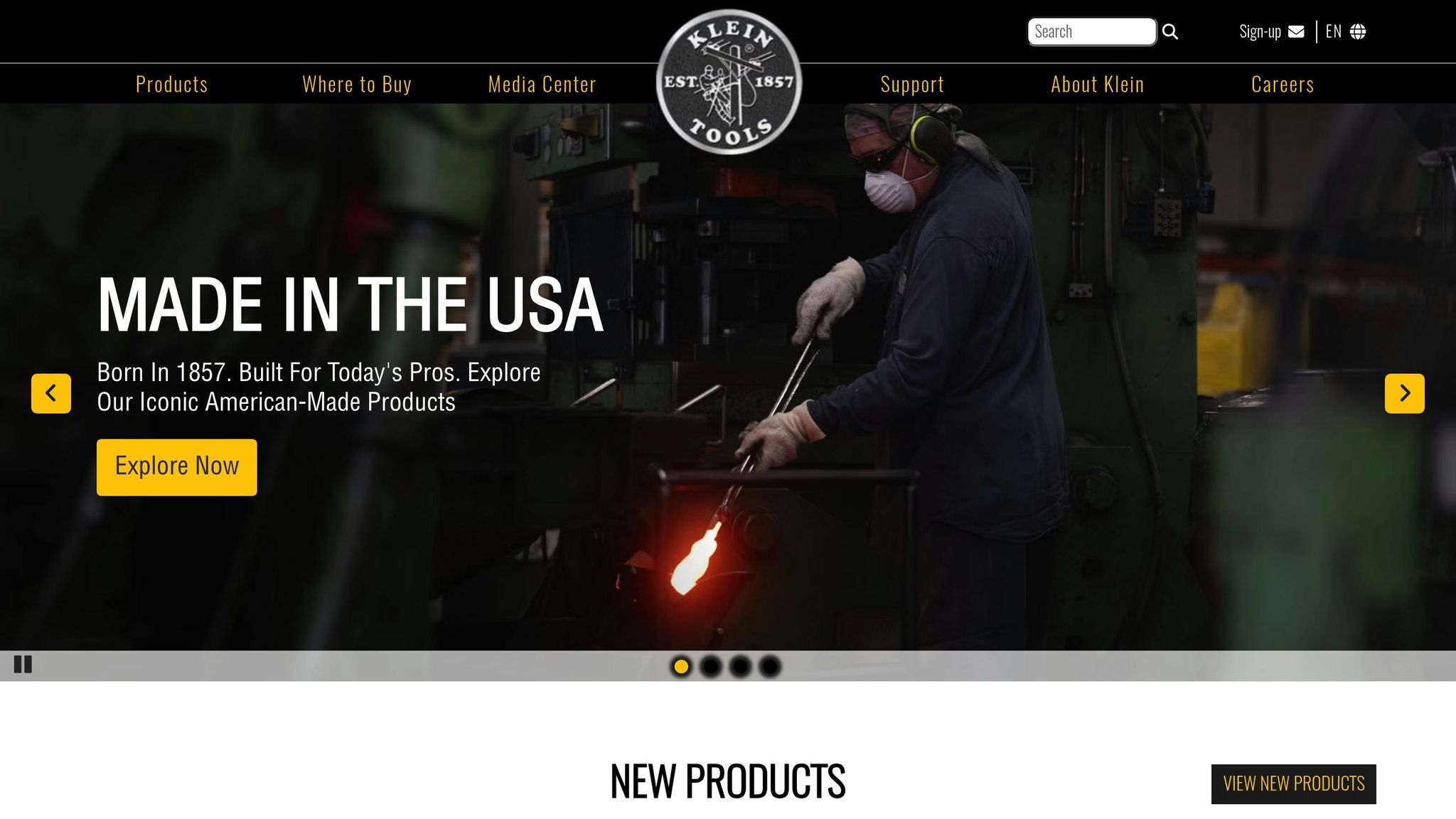
The Klein Tools Scout Pro Max Network Cable Tester is designed for testing data, voice, and video cables, making it a versatile tool for network troubleshooting. It’s priced at $479.99 on Amazon and $499.99 at Lowe's, offering features that cater to both professionals and serious DIYers.
Fault Detection Capabilities
The Scout Pro Max uses Time Domain Reflectometry (TDR) technology to measure cable length and pinpoint faults with precision. Its accuracy is within ± (2% + 3 feet) under standard conditions. This makes it particularly useful for diagnosing issues in large-scale cable systems.
The tester can handle cable lengths up to 2,000 feet (610 meters), which covers everything from short patch cords to extensive infrastructure installations. It also performs wiremap testing, identifying issues like wiring errors, open circuits, and short circuits.
Supported Cable Types
"Scout Pro Max tests and troubleshoots RJ11, RJ12, RJ45, and F-connector terminated cables and provides analog and digital tone generation for cable tracing." - Klein Tools
This device supports both shielded and unshielded cables, making it suitable for data, voice, and video applications. Beyond simple connectivity tests, it performs hub blink testing, measures both active and passive Power over Ethernet (PoE), and even tests POTS (Plain Old Telephone Service) lines. It can also detect active network capabilities, adding to its range of functions.
User Interface and Display
The Scout Pro Max is equipped with a full-color backlit LCD screen that ensures readability in various lighting conditions. The display provides clear test results, cable measurements, and fault locations. The device also includes internal memory, allowing users to store and download test results for generating detailed reports.
Portability and Field Use
Weighing 15.8 ounces (447 grams) and measuring 8 inches long, 1.5 inches high, and 4 inches wide, the Scout Pro Max is compact enough to fit in a tool bag without being cumbersome. It comes with a carrying case to keep the tester and its components organized during transport. Built for tough environments, it can withstand drops from 6.6 feet (2 meters) and offers a battery life of approximately 15 hours in active use and 1 year in standby mode.
Real-World Performance
The tester includes 20 remote locators for cable identification, making it easier to trace and organize multiple cables in complex setups. On Amazon, it holds a 3.7 out of 5-star rating, reflecting mixed user feedback.
"Great tester compared to a Fluke Q-Tester I've used for years", shared Randy B., a verified Amazon buyer.
However, some users have pointed out limitations. For instance, the LAN test doesn’t provide IP or DHCP status and won’t function with POE-enabled ports. These constraints could be a concern for technicians needing more advanced diagnostics.
Practical Considerations
Klein Tools recommends visually inspecting RJ plugs before inserting them into the tester to prevent damage. Ensure that the contacts are recessed within the plug's plastic housing. Additionally, care should be taken when connecting 6-position plugs into 8-position jacks unless the plug is specifically designed for such use.
Up next, we’ll take a closer look at the Fluke Networks TS 90 Cable Fault Finder.
2. Fluke Networks TS 90 Cable Fault Finder

The Fluke Networks TS 90 Cable Fault Finder is a handy tool that combines fault location, cable management, and tone generation in one device. It can measure cable lengths up to 2,500 feet (762 meters) from one end and pinpoint the exact distance to opens or shorts across a variety of cable types.
Fault Detection Methods
This device uses Time Domain Reflectometry (TDR) technology with a 50 Ω drive and a 6 V pulse. Unlike traditional TDRs that display complex waveforms, the TS 90 provides straightforward distance readings. This makes it much easier for technicians, especially those unfamiliar with interpreting TDR patterns, to quickly identify issues. Its simplified design speeds up troubleshooting, a critical advantage for fieldwork.
The TS 90 operates at a maximum rate of 4 measurements per second, though this speed may drop to 2 seconds depending on the cable's size and uniformity. It also features SmartTone technology, which helps verify correct wire pairs. By shorting the far end of the cable, users can hear tone changes, confirming the correct pair.
Cable Compatibility and Range
This fault finder works with cables that have two or more conductors and an impedance range of 35 Ω to 330 Ω. It automatically adjusts for variations within this range. If the cable falls outside these parameters, the device may display incorrect readings or show "–Err" for cables that are too long to measure accurately. Below is a table summarizing the maximum lengths for various cable types:
| Cable Type | Maximum Length |
|---|---|
| CAT-5 Twisted Pair | 2,500 feet |
| 12/2 AC Wire | 2,000 feet |
| RG-6/U TV Coax | 1,000 feet |
| RG-174/U Coax | 500 feet |
For cables with significant signal loss, the maximum measurable length drops to 500 feet. The TS 90 also allows users to adjust the VOP (Velocity of Propagation) setting from -20- to -99-, with a default value of -66-, to accommodate different cable types.
Display Features and User Interface
The TS 90 is designed with simplicity in mind. Its large LED screen and one-button operation make testing quick and easy. Instead of overwhelming users with complex waveforms, the display provides clear distance readings, ensuring results are easy to understand - even for less experienced technicians.
Safety and Power Requirements
Safety is a key feature of the TS 90. It includes high voltage detection, which alerts users to energized pairs up to 250VAC with an audible alarm when connecting to live wires. The tone injection system uses standard audio frequencies and is powered by 4 AA alkaline batteries, offering around 50 hours of operation. A low battery indicator flashes when the voltage drops below 4.1 V, so you're never caught off guard during critical testing. Plus, its moisture-resistant construction ensures durability in challenging field environments.
Next, let’s look at a tool specifically designed for underground applications.
3. HD Electric UCT-8/K01 Underground Cable Fault Tester
The HD Electric UCT-8/K01 is a reliable tool for utility companies and contractors tasked with testing underground cables. This device specializes in DC leakage current testing on de-energized, shielded underground cables, making it easier to pinpoint faults effectively.
Underground Cable Testing Capabilities
The UCT-8/K01 is built to handle underground cables up to 1,500 feet (457 meters) in length, with an operating voltage range from 50V to 25kVAC line-to-ground. For 15kV, 1/0 XLPE cables, it can manage lengths up to 7,500 feet under specific configurations. Even for the longest cables, the charging process takes just 35 seconds, ensuring quick and efficient testing in the field.
Once charged, the device applies an 8kVDC test voltage to detect high-voltage faults with precision. Designed to operate at 50/60Hz frequencies, it’s fully compatible with North American power systems.
Fault Detection and Safety Features
Safety is a priority with the UCT-8/K01. The device automatically detects AC voltage before switching to DC testing mode, reducing risks during operation. Test results are displayed clearly on a large LED screen with an analog bar graph, showing statuses such as GOOD, HIGH LEAKAGE, or FAULT. Its AC voltage accuracy is rated at ±5% of the reading, ensuring dependable measurements.
Operational Design and Portability
Weighing only 3 lbs (1.36 kg) without probes, the UCT-8/K01 is easy to carry and use in the field. Its compact size - 14 inches long, 4.6 inches wide, and 4.1 inches high (36 cm x 12 cm x 10 cm) - makes it convenient for transport and storage. The device is designed for single hotstick operation, adding to its practicality for fieldwork.
The tester features a one-button operation and includes a built-in 8kV high-voltage source, powered by a replaceable 9V lithium battery. On a full charge, the battery supports around 40 tests on 300 feet of 250 Kcmil non-faulted cable, though this number may drop when testing faulted cables. A low battery indicator ensures users aren’t caught off guard during critical testing tasks.
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Test Voltage Output | 8kVDC |
| Operating Voltage Range | 50V–25kVAC line-to-ground |
| Max Cable Length Tested | 1,500 ft (457 m) |
| Battery Life | ~40 tests on 300 ft of 250 Kcmil cable |
| Weight (without probes) | 3 lbs (1.36 kg) |
| Dimensions | 14" L x 4.6" W x 4.1" H |
Pricing and Value Proposition
Priced at $2,047.87, the UCT-8/K01 is a cost-effective solution for contractors and utility companies. Its built-in high-voltage source eliminates the need for external equipment, streamlining the testing process. The device’s simple pass/fail results make it an excellent choice for routine maintenance and troubleshooting, enabling quick and informed decisions.
Next, we’ll take a look at a versatile tool designed for network cable testing.
4. Fluke Networks MicroMapper
The Fluke Networks MicroMapper is a compact handheld cable tester built to verify Ethernet twisted pair cables in network setups. It specializes in wiremap verification and detecting basic faults, making it a practical tool for network professionals. Below, we’ll break down its key features, including testing capabilities, display functions, portability, and user feedback.
Cable Testing and Fault Detection
The MicroMapper is designed to pinpoint cable faults that can disrupt network connections. It checks twisted pair cables for common issues like open circuits, shorts, crossed pairs, reversed pairs, and split pairs. It also ensures cables meet TIA568A/B standards. One standout feature is its ability to detect split pairs in cables as short as 2 feet (0.6 meters), a rare capability in this category.
User Interface and Display
The device uses LED indicators to display wiremap results and identify faults such as opens, shorts, and split pairs. It can also measure cable lengths ranging from 1.31 feet to an impressive 656.17 feet. This straightforward interface makes it easy to interpret results quickly.
Portability and Field Use
Designed for convenience, the MicroMapper is lightweight and compact, measuring 4.9" x 2" x 1.2" and weighing just 4.59 ounces. Its portability is further enhanced by a remote unit that allows one-person testing of installed cables. The device also features a dual-tone mode for tracing hidden cables in dense setups. Powered by AAA alkaline batteries, it includes a low battery indicator and an auto-sleep function to conserve battery life during fieldwork.
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Cable Length Range | 1.31 ft – 656.17 ft |
| Dimensions | 4.9" x 2" x 1.2" |
| Weight | 4.59 oz |
| Minimum Split Pair Detection | 2 ft (0.6 m) |
| Power Source | AAA alkaline batteries |
Market Reception and Value
With a 4.5-star rating from 293 Amazon reviews, the MicroMapper is priced between $173 and $175. Customers praise its durable design, user-friendly interface, and reliable performance for basic cable testing. The package includes the MicroMapper device, a remote unit, a patch cable, a 6-volt alkaline battery, and a user guide. It is specifically built for Ethernet twisted pair cabling and supports RJ-45 network ports, making it a practical choice for network professionals.
sbb-itb-501186b
5. Fluke Networks IntelliTone
The Fluke Networks IntelliTone Pro 200 is a versatile cable tracing tool that combines digital and analog signals, making it a valuable addition to the lineup of tools we've discussed so far. This dual-mode functionality makes it highly effective for working with a wide variety of cable types, all while reducing interference from noise and minimizing false signals.
Cable Tracing and Fault Detection Capabilities
The IntelliTone Pro 200's SmartTone analog mode stands out by isolating wire pairs. It achieves this by changing the tone when it detects a short, making it easier to distinguish individual cables in bundled setups. Additionally, its integrated pair tester identifies wiring faults, and LED indicators help pinpoint specific cables within bundles. The CABLEMAP feature further enhances its capabilities by identifying common cable miswires. With clear LED indicators and tones, it confirms cable locations, checks continuity, and detects issues like opens, shorts, and reversed pairs.
Supported Cable Types and Versatility
This tool supports a broad range of copper cabling, making it suitable for both high-speed data networks and voice-grade applications. Here's a breakdown of its compatibility:
| Cable Type | Recommended Toning Method | Primary Application |
|---|---|---|
| Cat 5e/6/6a | Digital | High-speed data networks |
| Cat 3 and below | Analog | Voice communication systems |
| Coaxial | Analog | Video and data transmission |
| Security/Alarm | Analog | Security system installations |
| Speaker Wiring | Analog | Audio system connections |
The digital mode is particularly reliable for high-grade data cabling, such as Cat 5e, Cat 6, and Cat 6a, as it performs well even under common mode termination, where analog signals often struggle. This makes the IntelliTone Pro 200 an excellent choice for diagnosing 10/100 Gigabit Ethernet link connectivity, thanks to its NIC/hub indication features. Its ability to handle both high-speed data and voice-grade applications ensures it can adapt to various network environments seamlessly.
Ease of Use and User Experience
The IntelliTone Pro 200 has received a strong user rating of 4.3 out of 5 stars from 961 Amazon reviews. Users frequently highlight its performance on active networks and its efficiency in tracing wires over long distances. The automated toning of individual cable conductors makes locating cables quick, efficient, and safe, even on live networks. For example, one user shared:
"This is the most versatile tester we have in use... By using the tone sender we identified the older set of outlets location within the FD rack and also identified the newest set of outlets had not been terminated to the CP." – Rob Tutt, DEEWR
The IntelliTone Pro 200 comes with a variety of adapters and patch cables, including coax F, RJ11, and RJ45 connectors, along with an RJ45 input on the probe for direct patch panel connections. While most users praise its reliability and effectiveness, some have suggested that the instruction sheet could be more detailed and noted occasional inconsistencies in build quality.
Overall, the IntelliTone Pro 200 is a reliable tool for tracing voice, audio, and video cabling, offering the flexibility to work safely on active networks without causing disruptions.
"IntelliTone eliminates hours of cable confusion - and you can count on getting it right the first time." – Fluke Networks
Next, we'll explore the overall advantages and challenges of these cable testing solutions.
Advantages and Disadvantages
When it comes to cable fault testing tools, each option has its own set of strengths and weaknesses. The choice ultimately depends on your specific testing requirements and budget. Below, we’ll break down and compare these tools based on performance, cost, testing methods, ease of use, and durability.
Performance and Accuracy Comparison
Performance and accuracy are pivotal, especially in field applications where robust construction matters. Certification testers stand out by providing pass/fail results aligned with TIA/ISO standards, making them indispensable for commercial installations and warranty compliance. On the other hand, qualification testers determine whether existing cabling can handle required network speeds, which is particularly useful for troubleshooting bandwidth issues - though they come at a higher price. Lastly, verification testers handle basic continuity tests and help identify installation flaws like split pairs, but they don’t offer bandwidth-related insights.
Cost Analysis and Value Proposition
Cable testing tools span a wide price range based on features and functionality. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Tool Category | Price Range | Best Value Option |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Network Testers | $29.97 - $54.97 | Klein Tools LAN Explorer ($29.97) |
| Mid-Range Testers | $89.98 - $184.98 | Klein Tools VDV Scout Pro 3 ($184.98) |
| Professional Grade | $335.60+ | Fluke Networks IntelliTone Pro 200 ($335.60) |
Investing in cable testing equipment and training is no small expense. Routine testing is essential for keeping networks running smoothly and avoiding costly failures. Tools like the Advanced Cable Tester v2 offer a cost-effective solution by combining multiple tests into one device. For comparison, oscilloscopes capable of similar signal integrity tests can exceed $100,000.
Method-Specific Advantages and Limitations
Different testing methods come with their own pros and cons:
- Induction methods: Easy to use but may struggle with high-resistance faults and interference.
- Acoustic methods: Effective for high-impedance issues but require skilled technicians and strict safety protocols.
- Bridge methods: Highly accurate for low-voltage tests but less effective for high-impedance grounding.
- Pulse reflection: Quick and versatile for various voltage ranges but demands precise instruments and trained operators.
Operational Complexity and User Requirements
The complexity of operation varies widely between tools. Basic models are straightforward and require minimal expertise, while advanced tools offer detailed diagnostics but demand specialized training. Fluke Networks is a standout brand, known for delivering testers that balance accuracy, durability, and user-friendly design.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Professional-grade testers are built tough for fieldwork but require careful handling and regular calibration to maintain their accuracy. Basic testers, while easier to maintain, may need more frequent replacement in harsh environments. The growing demand for reliable cable testing solutions is reflected in the U.S. market, which was valued at $0.5 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit $0.9 billion by 2033.
Application-Specific Suitability
Choosing the right cable tester depends heavily on your network’s requirements and the types of cables in use. For simple faults, secondary pulse testers might be enough, while more complex networks benefit from the precision of three-pulse testers. Additionally, the method of cable installation - direct burial, pipe laying, trenching, or bracket setups - can influence the ease and accuracy of fault detection. Network testers remain essential for identifying physical layer issues, ensuring smooth data transmission, and catching problems before they escalate into full-blown network failures. Aligning the tool’s capabilities with your specific needs ensures efficient and effective testing.
Conclusion
Choosing the right cable fault testing tool boils down to understanding your specific operational needs and budget. For underground professionals working with LV, MV, and HV cables, tools that combine time domain reflectometers (TDR) with impulse current methods are highly effective for accurate fault detection. If precision mapping of underground utilities is your goal, RTK-enabled locators provide centimeter-level accuracy, catering to a wide range of budgets - from affordable to high-end professional devices. Knowing these requirements is critical for both underground and network applications.
For network technicians, selecting the right tool depends on the cable type - whether it’s Cat 5, Cat 6, or fiber optic. Basic continuity testers work for simple connectivity checks, but when detailed performance metrics and compliance checks are needed, advanced qualification and certification testers are a must. Each tool, whether designed for underground mapping or network fault detection, addresses a unique set of challenges.
Your work environment also plays a big role in the decision-making process. Field technicians often need rugged, portable tools that can handle tough conditions, while indoor specialists may prefer feature-packed desktop models. Brands like Megger offer vehicle-installed systems for robust on-site diagnostics, while handheld instruments are ideal for quick, on-the-go fault resolution.
While budget considerations are important, it’s crucial not to compromise on essential features. High-precision models may cost more upfront, but they save time and reduce downtime by delivering faster and more accurate results. Basic network testing tools might suffice for smaller installations, but professional-grade devices offer the durability and accuracy needed for larger, more complex systems.
The capabilities of the tools you choose should align with your testing needs. For example, TDRs are excellent for estimating fault locations, while surge generators and specialized receivers are indispensable for pinpointing faults. Regular cable testing not only prevents network failures but also ensures operational efficiency, making the right tool an investment in long-term reliability.
Whether you're addressing network connectivity issues or locating underground power cable faults, the right testing tools can simplify your work and minimize downtime. Consider your cable types, testing requirements, and work environment carefully to make the best choice for your needs.
FAQs
What sets Time Domain Reflectometry (TDR) apart from other cable fault detection methods?
Time Domain Reflectometry (TDR)
Time Domain Reflectometry (TDR) is a go-to technique for pinpointing cable faults with impressive precision. Here's how it works: a signal is sent through the cable, and any reflections caused by impedance changes are analyzed. These reflections help identify problems like open circuits or short circuits with a high degree of accuracy.
While other methods like Frequency Domain Reflectometry (FDR) or loop tests have their strengths - such as measuring impedance or evaluating overall cable performance - they aren't as effective when it comes to locating faults with precision. TDR's ability to detect faults in real time makes it an essential tool for diagnosing and resolving cable issues swiftly, especially when precision is non-negotiable.
How can I choose the right cable fault testing tool for my needs and budget?
Choosing the Right Cable Fault Testing Tool
Selecting the best cable fault testing tool boils down to understanding your specific needs - what types of cables you’re working with, the level of precision required, and how much you’re willing to spend. Start by identifying the cables you’ll be testing, whether they’re electrical, fiber optic, or Ethernet. If your tasks are straightforward, a simple continuity tester, often priced under $200, can get the job done. But if you’re tackling more advanced diagnostics, Time Domain Reflectometers (TDR) might be the better choice. These tools provide pinpoint fault location but come with a higher price tag.
When comparing tools, pay attention to features like detection range, ease of use, and whether the device is compatible with the cables you use most. If your work involves complex systems or demands exceptional accuracy, investing in professional-grade tools could save you time and effort in the long run. Balancing your technical needs with your budget ensures you’ll find a tool that’s up to the task.
What should I consider when testing underground cables versus network cables?
When examining underground cables, it's crucial to account for their exposure to challenging conditions such as moisture, soil, and physical stress. Testing typically targets insulation strength, resistance to moisture, and signs of physical damage. Common methods include insulation withstand tests and sheath integrity tests. Voltage withstand testing is particularly important during the commissioning phase to ensure reliability.
For network cables, the emphasis shifts to performance and connectivity. These tests focus on continuity, signal quality, and bandwidth capacity. Tools like multimeters or network testers are commonly used. Unlike underground cables, network cables are usually tested in controlled environments, with a strong focus on maintaining signal integrity and efficient data transmission.
The key distinction lies in the testing goals: underground cables demand durability and safety evaluations due to their harsh surroundings, while network cables are assessed for their ability to transmit data efficiently and maintain strong connectivity.
Related posts
- Electrical Equipment Inspection Checklist
- Ultimate Guide to Low Voltage Equipment
- Step-by-Step Circuit Breaker Testing Guide
- Top 7 Tools for Electrical Device Calibration