
Voltage Regulators vs Voltage Stabilizers
Share
Voltage fluctuations can damage your electronics or disrupt their performance. To prevent this, you have two options: voltage regulators and voltage stabilizers. Here’s the difference:
- Voltage Stabilizers: Adjust output voltage to stay within a safe range during power fluctuations. Ideal for homes and basic appliances.
- Voltage Regulators: Deliver a precise, constant voltage for sensitive electronics, regardless of input changes. Perfect for industrial and high-tech devices.
Quick Comparison
| Feature | Voltage Stabilizer | Voltage Regulator |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Stabilizes voltage within a range | Provides fixed, precise voltage |
| Response Time | Slower (gradual adjustment) | Faster (instant correction) |
| Accuracy | ±1% to ±0.5% (servo type) | ±1.5% to ±4% |
| Best Use | Home appliances, office equipment | Sensitive electronics, industrial |
| Maintenance | Regular servicing needed | Low maintenance |
| Cost | More affordable | Typically more expensive |
Key takeaway: Choose a voltage stabilizer for areas with frequent power dips or unstable grids. Opt for a voltage regulator when precision and speed are critical for protecting sensitive devices.
What Are Voltage Regulators?
Definition and Primary Function
A voltage regulator is a device designed to keep output voltage steady, no matter the changes in input voltage or load conditions. It uses a feedback loop to compare the output voltage to a reference level and adjusts as needed. If there’s any variation, the regulator modifies its control element to fix the issue, ensuring equipment consistently receives the exact voltage it needs.
"The voltage regulator is needed to keep voltages within the prescribed range that can be tolerated by the electrical equipment using that voltage." – Sujeet Srivastava
Unlike voltage stabilizers, which maintain voltage within a permissible range, voltage regulators ensure a precise, fixed output, making them ideal for precision circuits.
Let’s dive into the main types of voltage regulators.
Types of Voltage Regulators
Voltage regulators fall into two primary categories: linear and switching.
Linear regulators act like adjustable resistors, dissipating extra voltage as heat to maintain a stable output. They rely on a pass device (like a BJT or MOSFET) to regulate voltage. Linear regulators are simple, affordable, and produce minimal noise, but they’re less efficient because of the heat generated during operation.
Switching regulators, on the other hand, use a different mechanism. They rapidly switch a series element on and off, employing PWM (pulse-width modulation) to efficiently manage energy delivery. This makes them versatile, capable of stepping voltage up, stepping it down, or performing both (buck-boost conversion).
Some specialized types include:
- LDO (Low-Dropout) regulators – Designed to work with minimal voltage differences between input and output.
- Buck converters – Step down higher input voltages for lower output levels, like converting 12V to 5V for microcontrollers.
- Boost converters – Step up lower input voltages, often used in devices like solar chargers and power banks.
- Buck-boost converters – Handle both step-up and step-down tasks, useful for wide input voltage ranges.
Here’s a quick comparison of linear and switching regulators:
| Feature | Linear Regulators | Switching Regulators |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | Low | High |
| Design Complexity | Simple | Complex |
| Cost | Low | High |
| Noise Level | Low | Higher |
| Conversion Types | Step-down only | Step-up, Step-down, Buck-Boost |
| Heat Generation | Higher | Lower |
Now, let’s explore where these regulators are commonly used.
Applications of Voltage Regulators
Voltage regulators play a crucial role in delivering stable voltage across a variety of systems. In consumer electronics, linear regulators are often used in low-power devices that need minimal noise, such as portable audio players and radio receivers. LDO regulators, in particular, are essential for battery-powered gadgets like smartphones.
For industrial and automotive systems, switching regulators are preferred due to their ability to handle fluctuating input conditions. In automotive electronics, they ensure stable performance during engine start-up and operation, protecting sensitive systems from voltage spikes or drops.
Voltage regulators are also vital in data centers and servers, where energy efficiency is critical, and in renewable energy setups, where buck-boost converters stabilize power output despite inconsistent energy generation. Additionally, they’re indispensable in medical equipment and communication devices, where precise voltage regulation ensures safe and uninterrupted operation.
What Are Voltage Stabilizers?
Definition and Functionality
A voltage stabilizer is a device designed to keep the output voltage steady, even when the incoming voltage fluctuates. It adjusts the voltage within a specific range, ensuring that connected equipment gets a consistent power supply despite variations caused by grid issues, changing loads, or external factors like weather conditions.
Unlike voltage regulators, which provide a fixed output, stabilizers are dynamic, adapting to unpredictable voltage swings. Their job is to protect devices from the damage and inefficiency caused by unstable power.
"The primary function of a voltage stabilizer is to ensure that the output voltage remains within a specified range, providing a consistent and reliable power supply to connected electrical equipment." - Electrosheriff
This protection is vital, especially when you consider that voltage irregularities can lead to unplanned outages. Such disruptions can cost businesses an average of $260,000 per hour and often take at least four hours to resolve.
"Voltage stabilisers stop 'dirty voltage' from compromising the equipment's performance, operationality, and reliability. They are essential power conditioning devices that prevent sudden breakdowns and risky incidences." - Ashley Edison
Now, let’s explore the different types of voltage stabilizers and their specific uses.
Types of Voltage Stabilizers
Voltage stabilizers come in various designs, each suited for particular needs in terms of accuracy and response speed:
- Relay-based stabilizers: These are the most budget-friendly option. They rely on electromechanical relays to switch between voltage levels, making them suitable for basic home appliances that experience minor fluctuations. However, their output variation typically ranges between 5% and 10%.
- Servo-controlled stabilizers: Combining a servo motor with transformer technology, these stabilizers offer high precision (±1%) and can handle a wide input range (±50%). Controlled by a microcontroller, they adjust the autotransformer’s position to stabilize voltage. They are ideal for industrial applications and sensitive electronics but are more expensive and require regular maintenance.
- Static stabilizers: Using advanced solid-state electronics and microprocessors, static stabilizers provide the fastest voltage corrections. They adjust a multitap transformer's turn ratio using silicon-controlled rectifiers (SCRs). With no moving parts, they require minimal maintenance and are perfect for high-end appliances and medical equipment.
| Feature | Relay-Based | Servo-Controlled | Static |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Lower (5–10%) | High (±1%) | High |
| Response Time | Slow | Rapid | Very Fast |
| Maintenance | Low | Regular | Low |
| Cost | Affordable | High | Higher |
| Best Application | Home appliances | Industrial equipment | Medical/high-end devices |
Applications of Voltage Stabilizers
These stabilizers are indispensable across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. Here’s how they’re used in different settings:
- Industrial facilities: They counteract voltage drops over long cables and protect costly machinery from power fluctuations.
- Food & Beverage industry: Stabilizers ensure smooth production and consistent product quality by maintaining uninterrupted power.
- Broadcasting stations: Magnetic induction stabilizers are ideal for remote areas, ensuring reliable transmission where maintenance access is limited.
- Test laboratories: Precision stabilizers are crucial here, as even slight voltage variations can affect sensitive equipment and compromise measurement accuracy.
- IT sector: Data centers and server rooms rely on servo stabilizers to maintain stable voltage levels, ensuring uninterrupted data processing and system reliability.
- Telecommunication networks: Stabilizers minimize service disruptions caused by voltage fluctuations, ensuring consistent network performance.
When choosing a voltage stabilizer, key factors to consider include the output voltage range, load capacity, efficiency, size, price, reliability, safety features, and technical support. These considerations help ensure the stabilizer meets the specific needs of your application, offering reliable protection for your equipment. This adaptability sets stabilizers apart from voltage regulators, which focus on delivering fixed, precision-controlled outputs.
Static Voltage Stabilizer and regulators. [ Detail Guide]. IGBT based PWM method.
sbb-itb-501186b
Key Differences Between Voltage Regulators and Voltage Stabilizers
Voltage stabilizers and voltage regulators serve distinct purposes when it comes to managing voltage. Stabilizers ensure output remains within a safe range during input fluctuations, while regulators deliver a constant output regardless of changes in input voltage or load conditions. Knowing these differences can help you make the right choice for your equipment.
Regulators are designed for quick, almost instantaneous corrections, making them ideal for sensitive electronics. On the other hand, stabilizers adjust more gradually, which works well for household appliances and less sensitive devices.
Servo-based stabilizers offer high precision, with accuracies ranging from ±1% to ±0.5%, while Automatic Voltage Regulators (AVRs) typically operate within a broader accuracy range of ±1.5% to ±4%.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Voltage Stabilizer | Voltage Regulator (AVR) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Keeps output stable during input changes | Ensures constant output regardless of input or load |
| Response Time | Gradual adjustments | Immediate response |
| Accuracy | ±1% to ±0.5% (servo-based) | ±1.5% to ±4% (AVR) |
| Operation | Fully automatic, no manual input needed | May include manual adjustment options |
| Noise Level | Noticeable (servo type) | Minimal (solid-state) |
| Maintenance | Requires regular servicing | Low maintenance |
| Technology | Servo motorized systems | Microprocessor-controlled |
| Cost | Generally more affordable | Typically more expensive |
| Protection | Safeguards against overvoltage, undervoltage, and overload | Limited active protection |
These distinctions highlight how stabilizers and regulators cater to different needs, which becomes clearer when examining their use cases.
Use Case Scenarios
Your choice between a voltage stabilizer and a voltage regulator should align with the specific demands of your application, whether it’s about performance, precision, or maintenance.
For areas prone to unstable power grids or frequent voltage drops, voltage stabilizers are a solid option. They are especially useful in manufacturing environments where servo-controlled stabilizers can protect machinery and ensure smooth production despite grid fluctuations.
When working with sensitive electronics, such as laboratory equipment, medical devices, or advanced electronic systems, voltage regulators are the better choice. These devices provide instant corrections and maintain consistent output, ensuring reliable performance even with minor voltage variations.
Industrial settings often require tailored solutions. Stabilizers are an excellent fit for regions with frequent grid instability, as they provide robust protection against overvoltage and undervoltage. In contrast, regulators excel in applications that demand precise power control, such as debugging, testing, and specialized tasks.
Maintenance is another factor to consider. If technical support is limited, voltage regulators may be preferable due to their low upkeep requirements. Servo-controlled stabilizers, while effective, often need regular maintenance to function optimally.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Picking the right device means carefully assessing your electrical setup and the specific requirements of your equipment.
Factors to Consider
Precision Needs:
If you need ±1% voltage control, servo stabilizers are the way to go.
Equipment Sensitivity:
Sensitive industrial or commercial equipment often demands the precise control provided by servo stabilizers.
Load Type:
For three-phase motors, it’s crucial to identify the load type to select the correct capacity stabilizer.
Voltage Fluctuation Levels:
In areas prone to frequent grid instability, voltage stabilizers ensure a steady output. They protect appliances from fluctuations, helping extend their lifespan.
Response Time and Maintenance:
Voltage regulators are known for their quick response and lower maintenance needs, making them a cost-effective option. On the other hand, voltage stabilizers require regular upkeep and proper kVA ratings to function efficiently.
Energy Usage:
Servo stabilizers are energy-efficient, consuming little power and generating minimal heat. For instance, a stabilizer for a 1.5-ton AC typically uses about 15–20 watts.
To choose the right power rating, calculate the total wattage of your appliances, convert it to kVA, and factor in inrush currents. These steps can help you make an informed decision.
Availability Through Electrical Trader
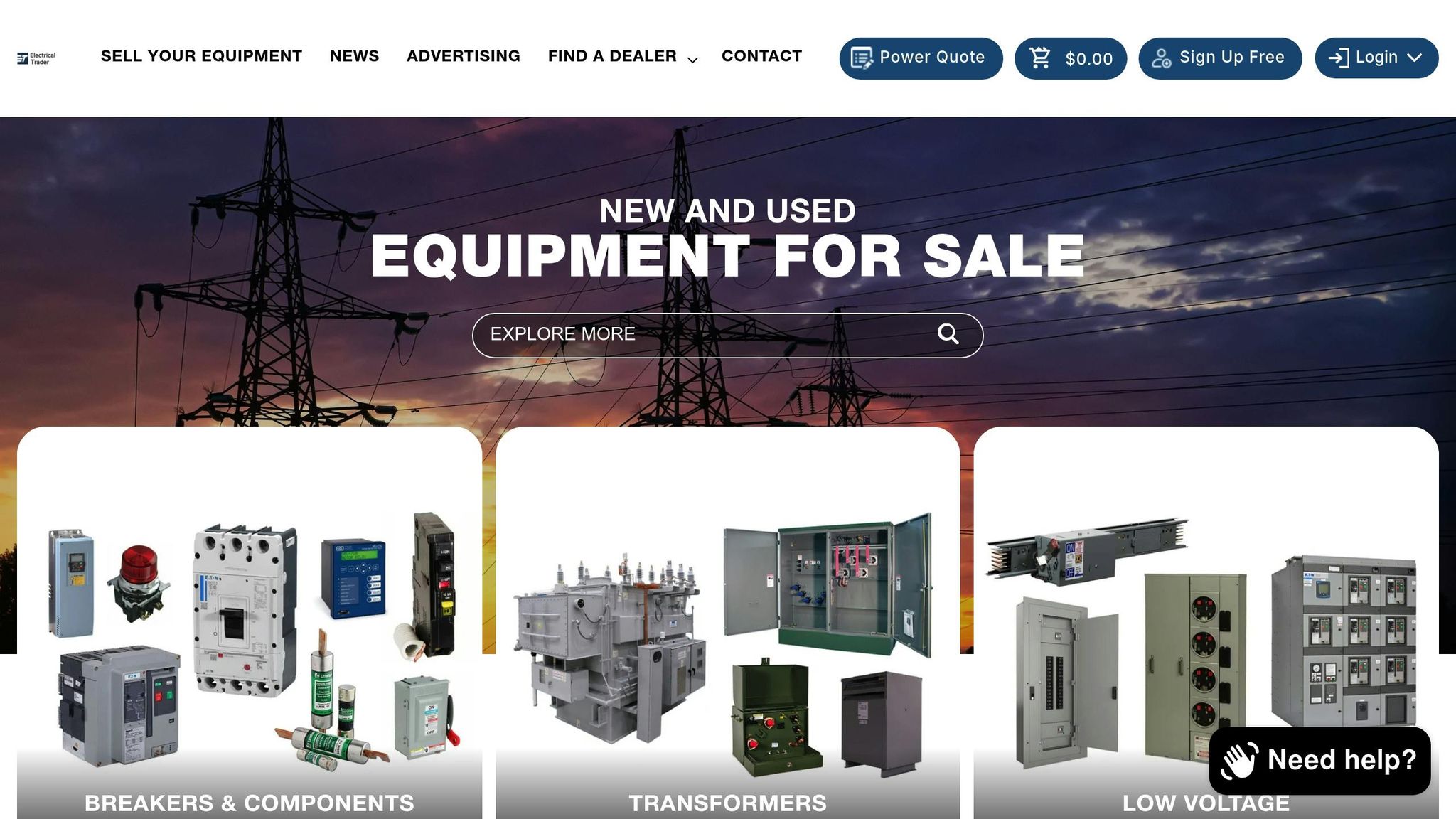
Electrical Trader makes finding the ideal voltage management solution straightforward. Their online marketplace offers a wide range of voltage regulators, stabilizers, and other power distribution equipment tailored to various needs. You’ll find both new and used electrical components, including transformers, breakers, and voltage equipment from trusted brands.
Whether you’re looking for a simple voltage regulator for your home or a high-precision servo stabilizer for industrial use, Electrical Trader’s user-friendly listings make the search easy. The platform caters to electricians, businesses, and individual users seeking dependable electrical equipment at competitive prices.
Plus, their resource center offers helpful buying guides to assist with your decision-making. You can compare options and specifications before purchasing, streamlining the process and ensuring you pick the right solution for your voltage management needs.
Conclusion
Voltage regulators and stabilizers play crucial roles in maintaining consistent and safe power levels for various devices. While voltage regulators are designed to provide a constant output for sensitive electronics like computers, medical devices, and laboratory instruments, voltage stabilizers are better suited for handling fluctuating input voltages, making them ideal for household appliances and office equipment in areas prone to power cuts and voltage dips.
The precision of these devices varies: regulators typically offer accuracy levels between ±1.5% and ±4%, while servo stabilizers achieve even tighter ranges of ±1% to ±0.5%. This level of precision should guide your choice depending on the specific demands of your equipment.
In short, your decision between a regulator and a stabilizer should hinge on your power stability needs and the sensitivity of your devices. Stabilizers are well-suited for environments with unstable mains voltage, protecting appliances from damage. On the other hand, voltage regulators are the go-to option for ensuring precise voltage supply to sensitive electronics.
For a wide selection of voltage regulators and stabilizers, Electrical Trader is a reliable source. Their online marketplace offers both new and used electrical components from trusted brands. Whether you're looking for a basic stabilizer for home appliances or a high-precision regulator for industrial applications, their platform provides the tools and variety to help you make an informed choice.
Visit Electrical Trader to explore their range of voltage management solutions and find the ideal product to keep your equipment running safely and efficiently.
FAQs
How can I decide if I need a voltage regulator or a voltage stabilizer for my home or business?
To choose between a voltage regulator and a voltage stabilizer, think about the kind of equipment you're using and the level of voltage control required.
A voltage regulator is the go-to option for sensitive electronics like computers, medical devices, or lab equipment. It delivers accurate and steady voltage by adapting to real-time fluctuations, making it perfect for applications where precision is critical.
On the other hand, a voltage stabilizer works well for household appliances like refrigerators, air conditioners, or televisions. It shields these devices from voltage spikes or dips by keeping the output within a preset safe range.
Take a close look at your equipment's power needs and the level of precision you require. If you're dealing with high-precision or delicate devices, a regulator is the better choice. For more general protection against voltage changes, a stabilizer will usually do the job. When in doubt, check your equipment's specifications or seek advice from an expert.
What kind of maintenance do voltage stabilizers and voltage regulators need?
Voltage stabilizers need regular maintenance to keep them running smoothly. This includes visual checks for signs of wear, corrosion, or physical damage, along with cleaning to avoid overheating issues. Most experts suggest performing these inspections once a year to maintain their efficiency.
Voltage regulators, by contrast, usually require less frequent maintenance. Depending on their usage and the conditions they operate in, occasional inspections of control systems and connections might be necessary.
Overall, voltage stabilizers demand more consistent care since they are built to manage power fluctuations and are often exposed to harsher environmental conditions. Keeping up with maintenance for both devices not only prolongs their lifespan but also ensures they operate reliably.
Can you use a voltage stabilizer and a voltage regulator together for better performance?
Using a voltage stabilizer and a voltage regulator together isn't usually a good idea. Both are designed to manage voltage, but they operate in different ways. When used simultaneously, they can interfere with each other, leading to issues like uneven load distribution that might damage your equipment.
It's better to pick the one that fits your needs. Voltage stabilizers work well for shielding household appliances from voltage swings, while voltage regulators are more suited for sensitive electronics that need precise voltage control. Choosing the right device for your specific situation will provide the protection and efficiency you need - without the complications of combining the two.
Related posts
- Ultimate Guide to Low Voltage Equipment
- High Voltage vs Low Voltage: Complete Comparison
- Voltage Regulation Problems: Causes and Fixes
- How to Choose an Isolation Transformer
